Natural Products
Daucosterol
| Catalog No. | CFN98713 | 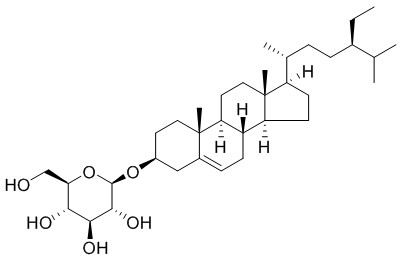 |
| CAS No. | 474-58-8 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 576.9 | |
| Molecular Formula | C35H60O6 | |
| DBs | [PubChem]:274951790 [ChEMBL]:67554 [PCIDB]:19308 |
Standard InChI:
InChI=1S/C35H60O6/c1-7-22(20(2)3)9-8-21(4)26-12-13-27-25-11-10-23-18-24(14-16-34(23,5)28(25)15-17-35(26,27)6)40-33-32(39)31(38)30(37)29(19-36)41-33/h10,20-22,24-33,36-39H,7-9,11-19H2,1-6H3/t21-,22-,24+,25+,26-,27+,28+,29-,30-,31+,32-,33-,34+,35-/m1/s1
Biological Activity
Daucosterol can protect mice against disseminated candidiasis by the CD4+ Th1 immune response.[1]
Daucosterol has proliferation-enhancing activity for neural stem cells (NSCs), may be involved in IGF1-AKT pathway, and it as an efficient and inexpensive growth factor alternative that could be used in clinical medicine and research applications.[2]
Daucosterol exhibits moderate antibacterial activity against Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus.[3]
Daucosterol can inhibit cancer cell proliferation by inducing autophagy through reactive oxygen species-dependent manner.[4]
Daucosterol has neuroprotective activity, could be potentially developed as a medicine for ischemic stroke treatment, can significantly reduce neuronal loss, as well as apoptotic rate and caspase-3 activity, increase the expression level of protein, diminish the down-regulation of p-AKT3 and p-GSK-3β4, thus activating the AKT5 signal pathway, diminish the down-regulation of the anti-apoptotic proteins Mcl-16 and Bcl-27, and decrease the expression level of the pro-apoptotic protein Bax8, thus raising the ratio of Bcl-2/Bax.[5]
Daucosterol has anti-cancer and apoptotic effects in human colon cancer cell line HCT-116, at different doses induces cell cycle arrest at sub-G1 phase of the cell cycle.[6]
Product
References
[1] Lee J H, Ju Y L, Ji H P, et al. Vaccine, 2007, 25(19):3834-40.
[2] Jiang L H, Yang N Y, Yuan X L, et al. J Steroid Biochem, 2014, 140(2):90-9.
[3] Sultana N, Afolayan A J. Nat Prod Res, 2007, 21(10):889-96.
[4] Zhao C, She T, Wang L, et al. Life Sci, 2015, 137:37-43.
[5] Jiang L H, Yuan X L, Yang N Y, et al. J Steroid Biochem 2015, 152:45-52.
[6] Wang G Q, Gu J F, Gao Y C, et al. Bangl J Pharmacol, 2016, 11(2).
[7] Hui-Ning L I, Liu H J, Xiao-Shuai F U, et al. 2013, 19(01):119-21.
Product Use Citation





