Natural Products
Linarin
| Catalog No. | CFN98738 | 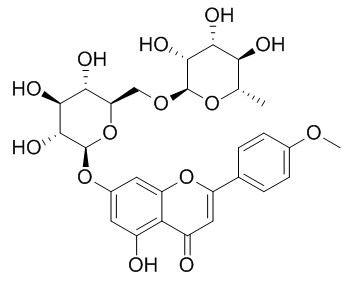 |
| CAS No. | 480-36-4 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 592.6 | |
| Molecular Formula | C28H32O14 | |
| DBs | [PubChem]:274951766 [ChEMBL]: [PCIDB]:4205 |
Standard InChI:
InChI=1S/C28H32O14/c1-11-21(31)23(33)25(35)27(39-11)38-10-19-22(32)24(34)26(36)28(42-19)40-14-7-15(29)20-16(30)9-17(41-18(20)8-14)12-3-5-13(37-2)6-4-12/h3-9,11,19,21-29,31-36H,10H2,1-2H3/t11?,19?,21-,22+,23-,24-,25?,26?,27+,28+/m0/s1
Biological Activity
Linarin is a flavone glycoside in the plants Flos chrysanthemi indici, Buddleja officinalis, Cirsium setosum, Mentha arvensis and Buddleja davidii, possesses analgesic, antipyretic, anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective activities. [1]
Linarin is known to have anti-acetylcholinesterase effects, prevents Aβ(25-35)-induced neurotoxicity through the activation of PI3K/Akt, which subsequently inhibits GSK-3β and up-regulates Bcl-2, may be a potent therapeutic compound against Alzheimer's disease acting through both acetylcholinesterase inhibition and neuroprotection.[2]
Linarin has dose-dependent analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities.[3]
Linarin can protect osteoblasts against hydrogen peroxide-induced osteoblastic dysfunction and may exert anti-resorptive actions, at least in part, via the reduction of RANKL and oxidative damage.[4]
Linarin induces the osteogenic differentiation and mineralization of MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells by activating the BMP-2/RUNX2 pathway through PKA signalingin vitroand protected against OVX-induced bone lossin vivo, suggests that linarin is a useful natural alternative for the management of postmenopausal osteoporosis.[5]
Product
References
[1] Lou H, Fan P, Perez R G, et al. Bioorgan Med Chem, 2011, 19(13):4021-7.
[2] Martínez-Vázquez M, Ramírez Apan T O, Lastra A L, et al. Planta Medica, 1998, 64(2):134-7.
[3] Kim Y H, Lee Y S, Choi E M. Cell Immunol, 2011, 268(2):112-6.
[4] Feng X, Wang X, Liu Y, et al. Iran J Pharm Res, 2015, 14(3):949-54.
[5] Li J, Hao L, Wu J, et al. Int J Mol Med, 2016, 37(4):901-10.
[6] Guo Q, Fang H, Shen H. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2010, 35(9).
Product Use Citation





