Natural Products
Caffeic acid
| Catalog No. | CFN99190 | 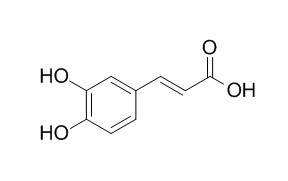 |
| CAS No. | 331-39-5 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 180.15 | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H8O4 | |
| DBs | [PubChem]:274951228 [ChEMBL]:36281 [PCIDB]:615 |
Standard InChI:
InChI=1S/C9H8O4/c10-7-3-1-6(5-8(7)11)2-4-9(12)13/h1-5,10-11H,(H,12,13)/b4-2+
Biological Activity
Caffeic acid is a well-known phenolic phytochemical present in many foods, including coffee, has anticarcinogenic effects, it can suppress ultraviolet B(UVB)-induced COX-2 expression by blocking Fyn kinase activity, suggests that this compound could act as a potent chemopreventive agent against skin cancer.[1]
Caffeic acid, has antioxidant activity, is an effective 2-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-
6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) radical scavenging, 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl free radical (DPPH ) scavenging, superoxide anion radical scavenging, total reducing power and metal chelating on ferrous ions activities.[2]
Caffeic acid has a stronger antioxidant activity than that of chlorogenic acid and chlorogenic acid is hydrolyzed into caffeic acid in the intestine, it is possible that caffeic acid plays a major role in the protective effect of chlorogenic acid against ischemia–reperfusion injury.[3]
Caffeic acid inhibits HBV-DNA replication as well as HBsAg production, also reduces serum DHBV level in DHBV-infected duckling model, suggests it has anti-HBV activity .[4]
Caffeic acid and some of its derivatives such as caffeic acid phenetyl ester (CAPE) and octyl caffeate are potent antioxidants which present important anti-inflammatory actions,
being their actions mediated, at least in part by the scavenging of NO and their ability to modulate iNOS expression and probably that of other inflammatory mediators.[5]
Caffeic acid exhibits a significant potential as an antidiabetic agent by suppressing a progression of type 2 diabetic states that is suggested by an attenuation of hepatic glucose output and enhancement of adipocyte glucose uptake, insulin secretion, and antioxidant capacity.[6]
Product
References
[1] Kang N J, Lee K W, Shin B J, et al. Carcinogenesis, 2009, 30(2):321-30.
[2] İlhami Gülçin. Toxicology, 2006, 217(2–3):213-20.
[3] Sato Y, Itagaki S, Kurokawa T, et al. Int J Pharm, 2011, 403(1–2):136-8.
[4] Wang G F, Shi L P, Ren Y D, et al. Antiviral Res, 2009, 83(2):186-90.
[5] Da C F, Duma D, Assreuy J, et al. Free Radical Res, 2009, 38(11):1241-53.
[6] Jung U J, Lee M K, Park Y B, et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2006, 318(2):476-83.
[7] Yong Y, Fang B H, Liu G C, et al. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Drug, 2014, 48(09):30-3.
Product Use Citation





