| In vitro: |
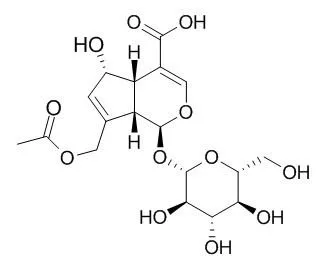
| Yakugaku Zasshi. 1981 Jul;101(7):657-9. | | Two novel glycosides from the fruits of Morinda citrifolia (noni) inhibit AP-1 transactivation and cell transformation in the mouse epidermal JB6 cell line.[Pubmed: 11479211] | The fruit juice of Morinda citrifolia (noni), a plant originally grown in the Hawaiian and Tahitian islands, has long been used by islanders to treat diseases, including cancer.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Two novel glycosides, 6-O-(beta-D-glucopyranosyl)-1-O-octanoyl-beta-D-glucopyranose and Asperulosidic acid, extracted from the juice of noni fruits, were used to examine their effects on 12-O-tedtradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)- and epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced AP-1 transactivation and cell transformation in mouse epidermal JB6 cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results indicated that both compounds were effective in suppressing TPA- or EGF-induced cell transformation and associated AP-1 activity. TPA- or EGF-induced phosphorylation of c-Jun, but not extracellular signal-regulated kinases or p38 kinases, was also blocked by the compounds, indicating that c-Jun N-terminal kinases were critical in mediating TPA- or EGF-induced AP-1 activity and subsequent cell transformation in JB6 cells. | | J.Weed Sci.Tech., 1986, 31:280-6. | | Plant Growth Inhibitors in Catchweed Seeds and Their Allelopathy.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Two Asp-related iridoidglucosides, compounds A and B were isolated from the dormant seeds of catchweed. By chemical analysis, compound A was identified as Asperulosidic acid which was derived from Asp through the cleavage of a lactone ring, and compound B as deacetyl Asperulosidic acid produced through the deacetylation of Asperulosidic acid. Asperulosidic acid inhibited the seed germination and growth of seedlings of large crabgrass and alfalfa to the same degree as Asp, but did not inhibit white clover, while deacetyl Asperulosidic acid showed lower inhibitory effect on the tested plants than Asp and Asperulosidic acid. Furthermore, Asperulosidic acid showed similar inhibitory activity to Asp on the germination of catchweed seeds themselves.
CONCLUSIONS:
Since these compounds were only detected in the exudate obtained from the seed coat of catchweed seeds, inhibition of the germination and growth of lettuce placed together with catchweed seeds may be due to iridoidglucosides liberated from the latter seeds which have been soaked in water. | | Phytomedicine . 2019 Feb;53:274-285. | | Anti-renal fibrosis effect of asperulosidic acid via TGF-β1/smad2/smad3 and NF-κB signaling pathways in a rat model of unilateral ureteral obstruction[Pubmed: 30668407] | | Abstract
Background: Renal fibrosis is the most common pathway leading to end-stage renal disease. It is characterized by excess extracellular matrix (ECM) accumulation and renal tissue damage, subsequently leading to kidney failure. Asperulosidic acid (ASPA), a bioactive iridoid glycoside, exerts anti-tumor, anti-oxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities, but its effects on renal fibrosis induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) have not yet been investigated.
Purpose: This study aimed to investigate the protective effect of ASPA on renal fibrosis induced by UUO, and to explore its pharmacological mechanism.
Methods: Thirty-six Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were randomly divided into six groups: sham group, UUO model group, three ASPA treatment groups (10, 20, and 40 mg/kg), and captopril group (20 mg/kg). Rats were administered vehicle, ASPA or captopril intraperitoneally once a day for 14 consecutive days. Urea nitrogen (BUN), uric acid (UA) and inflammatory factors in serum samples were evaluated on the 7th, 10th, and 14th day after renal fibrosis induction. In addition, the 12 h urine was collected to test the content of urinary protein (upro) on the 14th day. The obstructive renal tissues were collected for pathological analysis (hematoxylin and eosion (H&E) staining and Masson's Trichrome staining) and immunohistochemical analysis on the 14th day after renal fibrosis induction. The mRNA expression of related factors and the protein levels of smad2, smad3, and smad4 were measured in UUO-induced rats by real time PCR and Western blot, respectively.
Results: The levels of BUN, UA, and upro were elevated in UUO-induced rats, but ASPA treatment improved renal function by reducing the levels of BUN, UA, and upro. The protein levels of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and IL-6, as well as the mRNA levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) and interferon-γ (IFN-γ), were decreased after ASPA administration (10, 20 and 40 mg/kg) in a dose-dependent manner. The ASPA exerted an alleviation effect on the inflammatory response through inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathway. In addition, reductions in α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), collagen III, and fibronectin expression were observed after ASPA administration at doses of 20 and 40 mg/kg. Furthermore, the renal expression of transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), smad2, smad3, and smad4 was down-regulated by ASPA treatment at doses of 20 and 40 mg/kg.
Conclusion: ASPA possessed protective effects on renal interstitial fibrosis in UUO-induced rats. These effects may be through inhibition of the activation of NF-κB and TGF-β1/smad2/smad3 signaling pathways.
Keywords: Asperulosidic acid; NF-κB signaling pathway; Renal interstitial fibrosis; TGF-β1/smad2/smad3 pathway; Unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO). | | Int J Mol Sci . 2018 Jul 12;19(7):2027. | | Asperuloside and Asperulosidic Acid Exert an Anti-Inflammatory Effect via Suppression of the NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways in LPS-Induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages[Pubmed: 30002289] | | Abstract
Hedyotis diffusa is a folk herb that is used for treating inflammation-related diseases in Asia. Previous studies have found that iridoids in H. diffusa play an important role in its anti-inflammatory activity. This study aimed to investigate the anti-inflammatory effect and potential mechanism of five iridoids (asperuloside (ASP), Asperulosidic acid (ASPA), desacetyl Asperulosidic acid (DAA), scandoside methyl ester (SME), and E-6-O-p-coumaroyl scandoside methyl ester (CSME)) that are presented in H. diffusa using lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced RAW 264.7 cells. ASP and ASPA significantly decreased the production of nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E₂ (PGE₂), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in parallel with the inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), TNF-α, and IL-6 mRNA expression in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. ASP treatment suppressed the phosphorylation of the inhibitors of nuclear factor-kappaB alpha (IκB-α), p38, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). The inhibitory effect of ASPA was similar to that of ASP, except for p38 phosphorylation. In summary, the anti-inflammatory effects of ASP and ASPA are related to the inhibition of inflammatory cytokines and mediators via suppression of the NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways, which provides scientific evidence for the potential application of H. diffusa.
Keywords: anti-inflammation; iridoids; mitogen-activated protein kinase; nuclear factor-kappaB. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)