Natural Products
Xanthatin
| Catalog No. | CFN98315 | 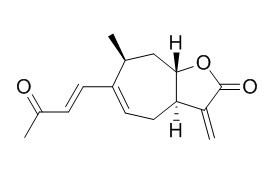 |
| CAS No. | 26791-73-1 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 246.3 | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H18O3 | |
| DBs | [PubChem]:274952105 [ChEMBL]:10058 [PCIDB]:3394 |
Standard InChI:
InChI=1S/C15H18O3/c1-9-8-14-13(11(3)15(17)18-14)7-6-12(9)5-4-10(2)16/h4-6,9,13-14H,3,7-8H2,1-2H3/b5-4+/t9-,13+,14-/m0/s1
Biological Activity
Xanthatin, a natural sesquiterpene lactone, has significant antitumor activity against a variety of cancer cells; it displays significant antitumor effects through cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction in A549 cells, these effects are associated with intrinsic apoptosis pathway and disrupted NF-κB signaling, suggests that it may have therapeutic potential against human non-small-cell lung cancer.[1]
Xanthatin has bactericidal and fungicidal activity, including against Colletotrichum gloesporoides, Trichothecium roseum, Bacillus cereus and Staphylococcus aureus.[2]
Xanthatin and the crude extracts of Xanthium strumarium have cytotoxic activity.[3]
(−)-Xanthatin is a highly effective inhibitor of MDA-MB-231 cell growth, inducing caspase-independent cell death, and that these effects were independent of FTase inhibition; GADD45γ was selectively induced by (−)-xanthatin and that GADD45γ-primed JNK and p38 signaling pathways are, at least in part, involved in mediating the growth inhibition and potential anticancer activities of this agent; GADD45γ is becoming increasingly recognized for its tumor suppressor function, suggests that the novel possibility that (−)-xanthatin may have therapeutic value as a selective inducer of GADD45γ in human cancer cells, in particular in FTI-resistant aggressive breast cancers.[4]
Xanthatin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human gastric carcinoma MKN-45 cells, it may have therapeutic potential against human gastric carcinoma.[5]
Xanthatin is a novel potent inhibitor of VEGFR2 signaling, can inhibit angiogenesis and tumor growth in breast cancer cells.[6]
Product
References
[1] Zhang L, Ruan J, Yan L, et al. Molecules, 2012, 17(4):3736-50.
[2] Ginesta-Peris E, Garcia-Breijo F J, Primo-Yúfera E. Lett Appl Microbiol, 1994, 18(4):206-8.
[3] Roussakis C, Chinou I, Vayas C, et al. Planta Med, 1994, 60(5):473-4.
[4] Takeda S, Matsuo K, Yaji K, et al. Chem Res Toxicol, 2011, 24(6):855-65.
[5] Zhang L, Tao L, Ruan J, et al. Planta Med, 2012, 78(9):890-5.
[6] Yu Y, Yu J, Pei C G, et al. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2015, 8(9):10355-64.
[7] Yan C, Li H, Yu W, et al. J Chromatogr B , 2014, s 947–948(2):57-61.
Product Use Citation





