Natural Products
Genistein
| Catalog No. | CFN98681 | 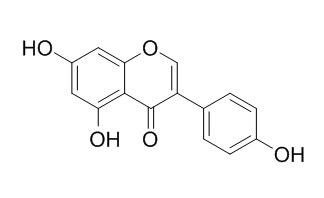 |
| CAS No. | 446-72-0 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 270.2 | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H10O5 | |
| DBs | [PubChem]:274951822 [ChEMBL]:28088 [PCIDB]: |
Standard InChI:
InChI=1S/C15H10O5/c16-9-3-1-8(2-4-9)11-7-20-13-6-10(17)5-12(18)14(13)15(11)19/h1-7,16-18H
Biological Activity
Genistein, the major phytoestrogen in soy, is linked to diminished female reproductive performance and to cancer chemoprevention and decreased adipose deposition; genistein-induces hypermethylation persisted into adulthood, decreases ectopic Agouti expression and protecting offspring from obesity, suggests that in utero dietary genistein affects gene expression and alters susceptibility to obesity in adulthood by permanently altering the epigenome.[1]
Genistein is a specific inhibitor of tyrosine-specific protein kinases, can inhibit the EGF-stimulated increase in phosphotyrosine level in A431 cells.[2]
Genistein down-regulates NF-kappaB and phospho-in , leading to the suppression of proliferation and induction of apoptosis, thus providing the molecular basis for the treatment of patients with this pharmacologically safe agent.[3]
Genistein exerts multiple suppressive effects on human breast carcinoma cells, suggests that its mechanism of chemoprevention is pleiotropic.[4]
Genistein stimulates estrogen-responsive pS2 mRNA expression at concentrations as low as 10(-8) M and these effects can be inhibited by tamoxifen; genistein competed with [3H]estradiol binding to the estrogen receptor with 50% inhibition at 5 x 10(-7) M, thus, the estrogenic effect of genistein would appear to be a result of an interaction with the estrogen receptor.[5]
Genistein inhibits TPA-induced COX-2 expression in MCF10A cells by blocking ERK-mediated phosphorylation of p65 and its subsequent interaction with CBP and TBP.[6]
Genistein has neuroprotective effect against beta amyloid-induced neurotoxicity.[7]
Product
References
[1] Dolinoy D C, Weidman J R, Waterland R A, et al. Environ Heal Persp, 2006, 114(4):567-72.
[2] Akiyama T, Ishida J, Nakagawa S, et al. J Biol Chem, 1987, 262(12):5592-5.
[3] He H, Chen L, Zhai M, et al. Phytother Res, 2009, 23(6):868–73.
[4] Shao Z, Jiong W U. Int J Cancer, 1998, 22(5):362-5.
[5] Wang T T, Sathyamoorthy N, Phang J M. Carcinogenesis, 1996, 17(2):271-5.
[6] Chung M H, Kim D H, Na H K, et al. Mutat Res Fund Mol M, 2014, 768:74-83.
[7] Bang O Y, Hong H S, Dong H K, et al. Neurobiol Dis, 2004, 16(1):21-8.
[8] Zhang H, Suo Z, Zhang Z, et al. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis. 2003,23(1):18-9.
Product Use Citation





