Natural Products
Aloeemodin
| Catalog No. | CFN98749 | 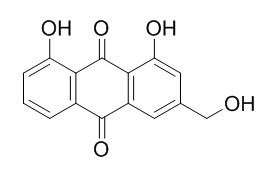 |
| CAS No. | 481-72-1 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 270.2 | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H10O5 | |
| DBs | [PubChem]:274951755 [ChEMBL]:2607 [PCIDB]:2789 |
Standard InChI:
InChI=1S/C15H10O5/c16-6-7-4-9-13(11(18)5-7)15(20)12-8(14(9)19)2-1-3-10(12)17/h1-5,16-18H,6H2
Biological Activity
Aloeemodin is able to interact with DNA under certain in vitro conditions, however, in vivo it is negative did not indicate a genotoxic potential, thus, it may be assumed that a genotoxic risk for man might be unlikely.[1]
Aloeemodin has inhibition of β-amyloid aggregation, and has neuroprotective effect on primary hippocampal cells against β-amyloid induced toxicity.[2]
Aloeemodin has anti-fibrotic effects, perhaps through downregulation of the expression of Smad2 mRNA and TGF-β1,TIMP1,and type Ⅰ and Ⅲ collagen proteins,and upregulation of the expression of Smad7 mRNA.[3]
Aloeemodin might have therapeutic effects on liver fibrosis induced by Schistosoma of liver through the effects of TGF-β1,VEGF and FAK expression.[4]
Aloeemodin can suppress the proliferation of HGC-27 cell to induce apoptosis and block cell cycle.[5]
Product
References
[1] Heidemann A, Völkner W, Mengs U. Mutation Research/fundamental & Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 1996, 367(3):123-33.
[2] Ho S L, Poon C Y, Lin C, et al. Current Alzheimer Research, 2015, 12(5):424-33.
[3] Wu Y Y, He S S. World Chinese Journal of Digestology, 2009, 17(27):2778-83.
[4] Dan X U, Zhou W, Hong-Gang Y U. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional & Western Medicine on Liver Diseases, 2012, 22(02):107-9.
[5] Nan J, Qin Y X, Liu J, et al. J Modern Oncol, 2008, 16(06):919-21.
[6]Chen C S, Sang X F. Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory Technology, 2011(05):1088-9.
Product Use Citation





