Natural Products
Kaempferol
| Catalog No. | CFN98838 | 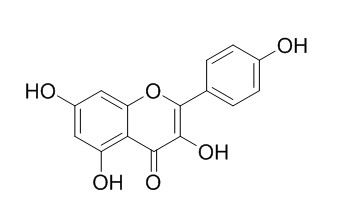 |
| CAS No. | 520-18-3 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 286.2 | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H10O6 | |
| DBs | [PubChem]:274951667 [ChEMBL]:28499 [PCIDB]:4565 |
Standard InChI:
InChI=1S/C15H10O6/c16-8-3-1-7(2-4-8)15-14(20)13(19)12-10(18)5-9(17)6-11(12)21-15/h1-6,16-18,20H
Biological Activity
Kaempferol is a polyphenol antioxidant found in fruits and vegetables, has beneficial effects in reducing the risk of chronic diseases, especially cancer, it may help to promote the development of cancer by augmenting the body's antioxidant defence against free radicals,and inhibit cancer cell growth and angiogenesis and induce cancer cell apoptosis.[1]
Kaempferol and quercetin have anti-inflammatory effects by modulating of iNOS, COX-2 and CRP, and involving blockade of NF-κB activation and the resultant up-regulation of the pro-inflammatory genes.[2]
Kaempferol is an autophagic enhancer, has a more general protection in Parkinson's disease, can mediate antiapoptotic and antioxidant effects is the enhancement of mitochondrial turnover by autophagy.[3]
Kaempferol and quercetin at concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 100 microM reduce bone resorption in a time and dose-dependent manner, have significant inhibitory effects at concentrations as low as 0.1 microM especially with kaempferol, they exert a potent inhibitory effect on in vitro bone resorption.[4]
Product
References
[1] Chen A Y, Chen Y C.Food Chem, 2013, 138(4):2099-107.
[2] García-Mediavilla V, Crespo I, Collado P S, et al. Eur J Pharmacol, 2007, 557(2–3):221-9.
[3] Filomeni G, Graziani I, Zio D D, et al. Neurobiol Aging, 2012, 33(4):767-85.
[4] Wattel A, Kamel S, Mentaverri R, et al. Biochem Pharmacol, 2003, 65(1):35-42.
[5] Yuanqing F U, Fengwei M O, Liao H. Medicinal Plant, 2013(1):42-43, 46.
Product Use Citation





