Natural Products
Piceatannol
| Catalog No. | CFN99024 | 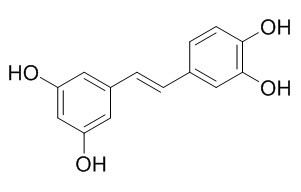 |
| CAS No. | 10083-24-6 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 244.2 | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H12O4 | |
| DBs | [PubChem]:274951483 [ChEMBL]:28814 [PCIDB]: |
Standard InChI:
InChI=1S/C14H12O4/c15-11-5-10(6-12(16)8-11)2-1-9-3-4-13(17)14(18)7-9/h1-8,15-18H/b2-1+
Biological Activity
Piceatannol , a resveratrol analogue, is a polyphenol present in the skins of grapes and in wine and other foods, it inhibits proliferation and migration of VSMC treated with TNF-α, therefore, piceatannol may be an effective therapeutic approach to treat atherosclerosis.[1]
Piceatannol inhibits the antigen-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of Syk and inhibit mast cell Fc epsilon R1-mediated signaling and effector function.[2]
Piceatannol is a closely related stilbene that has antileukaemic and anti-cancer activity, it is converted from resveratrol by the cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP1B1;resveratrol, as well as the hydroxylated analog piceatannol, are potent inducers of apoptotic cell death in BJAB Burkitt-like lymphoma cells with an ED50 concentration of 25 microM; piceatannol is a very efficient inducer of apoptosis in this ex vivo assay with leukemic lymphoblasts of 21 patients suffering from childhood lymphoblastic leukemia.[3,4]
Piceatannol sensitizes TRAIL-induced-apoptosis via Sp1- and ERK-dependent DR5 up-regulation. [5]
Piceatannol is an anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and anti-proliferative stilbene that has been shown to interfere withthe cytokine signaling pathway; piceatannol inhibits TNF-induced NF-κB activation and NF-κB-mediated gene expression through suppression of IκBα kinase and p65 phosphorylation.[6]
Piceatannol inhibits phorbol ester-induced NF-κB activation and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human breast epithelial cells, the cysteine 179 of IKKβ as a potential target.[7]
Piceatannol, resveratrol and 3,3',4,4',5,5'-hexahydroxy-trans-stilbene manifest potent antioxidant effects on three leukemic cell lines and the presence of ortho-dihydroxy structures enhanced the protective effect against DNA damage caused by .OH radicals.[8]
Piceatannol exerts much stronger protective effects on PC12 cells from oxidative stress than did resveratrol, piceatannol treatment attenuates the intracellular accumulation of ROS induced by treatment of PC12 cells with Beta-amyloid, inhibits Beta-amyloid-induced apoptotic features including internucleosomal DNA fragmentation, nucleus condensation, cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP), and activation of caspase-3. [9]
Product
References
[1] Lee B, Lee E J, Kim D I, et al. Toxicol in Vitro, 2009, 23(7):1284-91.
[2] Oliver J M, Burg D L, Wilson B S, et al. J Biol Chem, 1994, 269(47):29697-703.
[3] Potter G A, Patterson L H, Wanogho E, et al. Brit J Cancer, 2002, 86(5):774-8.
[4] Wieder T, Prokop A, Bagci B, et al. Leukemia, 2001, 15(11):1735-42.
[5] Kang C H, Moon D O, Choi Y H, et al. Toxicol in Vitro, 2011, 25(3):605-12.
[6] Ashikawa K, Majumdar S, Banerjee S, et al. J Immunol, 2002, 169(11):6490-7.
[7] Pilsoon S, Sinaye P, Na H K, et al. Carcinogenesis, 2010, 31(8):1442-9.
[8] Ovesná Z, Kozics K, Bader Y, et al. Oncol Rep, 2006, 16(3):617-24.
[9] Jin K H, Won L K, Joo L H. Ann NY Acad Sci, 2007, 1095(1):473-82.
[10] Liu B, Xie Y Q. China Medical Herald, 2009, 6(4):40-1.
Product Use Citation





