Natural Products
Demethoxycurcumin
| Catalog No. | CFN99185 | 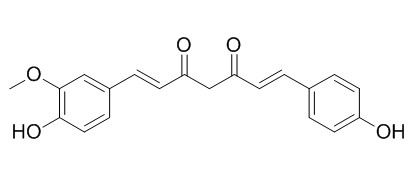 |
| CAS No. | 22608-11-3 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 338.35 | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H18O5 | |
| DBs | [PubChem]:274951233 [ChEMBL]:65737 [PCIDB]:37023 |
Standard InChI:
InChI=1S/C20H18O5/c1-25-20-12-15(6-11-19(20)24)5-10-18(23)13-17(22)9-4-14-2-7-16(21)8-3-14/h2-12,21,24H,13H2,1H3/b9-4+,10-5+
Biological Activity
Demethoxycurcumin (DMC) is one of the main active compounds of curcuminoids found in turmeric powder, which is used as a spice in Asian cooking and traditional medicine, has anti-inflammation and anti-cancer activities, the mechanism of DMC-mediated anti-invasive activity involves modulation of the expression of invasion-associated proteins, possibly by targeting NF-κB in MDA-MB-231 cells.[1]
Demethoxycurcumin has the relative potency for suppression of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-induced nuclear factor-B (NF-B) activation, the relative potency is curcumin > demethoxycurcumin> bisdemethoxycurcumin, they also exhibit variable anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative activities, which do not correlate with their ability to modulate the ROS status.[2]
Demethoxycurcumin, curcumin and bisdemethoxycurcumin have pro-oxidant, anti-oxidant and cleavage activities on DNA .[3]
Demethoxycurcumin (DMC) has differential potency for inhibition of cancer cell invasion, the differential potency is BDMC> or =DMC>Cur, whereas the cell migration is not affected, shows higher antimetastasis potency than curcumin by the differentially down-regulation of ECM degradation enzymes.[4]
Demethoxycurcumin exerts its in vitro anti-inflammatory effect in LPS-activated N9 microglial cells by blocking nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and MAPKs activation, which may be partly due to its potent down-regulation of the NADPH-derived iROS production.[5]
Demethoxycurcumin can induce the apoptosis of human lung cancer NCI-H460 cells through the mitochondrial-dependent pathway, it may be used as a novel anticancer agent for the treatment of lung cancer in the future.[6]
Product
Official website: Demethoxycurcumin
Japanese website: Demethoxycurcumin
Chinese website: Demethoxycurcumin
Japanese website: Demethoxycurcumin
Chinese website: Demethoxycurcumin
References
[1] Yodkeeree S, Ampasavate C, Sung B, et al. Eur J Pharmacol, 2009, 627(1-3):8-15.
[2] Sandur SK, Pandey MK, Sung B,et al. Carcinogenesis, 2007, 28(8):1765-73.
[3] Jayaprakasha G K, Rao L J, Sakariah K K. Food Chem, 2006, 98(4):720-4.
[4] Ahsan H, Parveen N, Khan N U, et al. Chem-biol interact, 1999, 121(2):161-75.
[5] Yodkeeree S, Chaiwangyen W, Garbisa S, et al. J Nutr Biochem, 2009, 20(20):87-95.
[6] Zhang L, Wu C, Zhao S, et al. Int Immunopharmacol, 2010, 10(3):331-8.
[7] Jadhav B K, Mahadik K R, Paradkar A R. Chromato, 2007, 65(7):483-8.
Product Use Citation





