Natural Products
Blumeatin
| Catalog No. | CFN99278 | 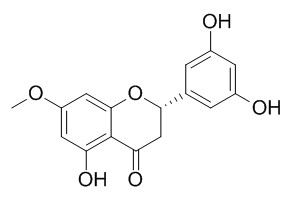 |
| CAS No. | 118024-26-3 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 302.3 | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H14O6 | |
| DBs | [PubChem]:274950872 [ChEMBL]: [PCIDB]: |
Standard InChI:
InChI=1S/C16H14O6/c1-21-11-5-12(19)16-13(20)7-14(22-15(16)6-11)8-2-9(17)4-10(18)3-8/h2-6,14,17-19H,7H2,1H3/t14-/m0/s1
Biological Activity
Blumeatin was first isolated from Blumea balsamifera DC, it can inhibit the increase of serum alanine aminotransferase (AAT) and liver triglyceride and increased serum triglyceride, beta-lipoprotein, and liver glycogen content in CCl4-intoxicated rats, and can shorten the pentobarbital sleeping time in CCl4-intoxicated mice; suggestes that blumeatin can protect liver against injury induced by CCl4 and TAA.[1]
Blumeatin can promote adipocyte differentiation as characterized by increased triglyceride levels in 3T3L1 cells, also enhances the accumulation of lipid droplets and induced upregulation of the expression of the adipocyte-specific genes aP2 and GLUT4.[2]
Blumeatin has antioxidant properties, free radical scavenging activity,and has xanthine oxidase (XO) inhibitory activity.[3,4]
Product
References
[1] Xu S B, Chen W F, Liang H Q, et al. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 1993, 14(4):376-8.
[2] Zhang L B, Ji J, Lei C, et al. J Nat Prod, 2012, 75(4):699-706.
[3] Nessa F, Ismail Z, Mohamed N, et al. Food Chem, 2004, 88(2):243-52.
[4] Nessa F, Ismail Z, Mohamed N. Pharm Biol, 2010, 48(48):1405-12.
[5] Nessa F, Ismail Z, Karupiah S, et al. J Chromatogr Sci, 2005, 43(8):416-20.
Product Use Citation





