Natural Products
Pachymic acid
| Catalog No. | CFN99590 | 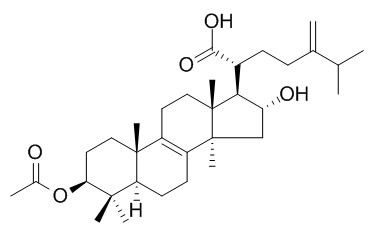 |
| CAS No. | 29070-92-6 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 528.76 | |
| Molecular Formula | C33H52O5 | |
| DBs | [PubChem]:274950563 [ChEMBL]:80885 [PCIDB]:23810 |
Standard InChI:
InChI=1S/C33H52O5/c1-19(2)20(3)10-11-22(29(36)37)28-25(35)18-33(9)24-12-13-26-30(5,6)27(38-21(4)34)15-16-31(26,7)23(24)14-17-32(28,33)8/h19,22,25-28,35H,3,10-18H2,1-2,4-9H3,(H,36,37)/t22-,25-,26+,27+,28+,31-,32-,33+/m1/s1
Biological Activity
Pachymic acid (PA) is a natural triterpenoid known to inhibit the phospholipase A2 (PLA(2)) family of arachidonic acid (AA)-producing enzymes, PA-treatment decreases bad phosphorylation, increases Bcl-2 phosphorylation, and activates caspases-9 and -3, it also decreases the expression and activation of proteins within the AKT signal pathway. suggests that PA initiates apoptosis through mitochondria dysfunction and influences apoptosis by reducing prostaglandin .[1]
Pachymic acid has hypoglycemic activity ,can stimulating glucose uptake, GLUT4 gene expression and translocation, and promoting triglyceride accumulation in adipocytes.[2]
Pachymic acid can exhibit antiinflammatory and anticancer properties, it can inhibit cell growth and modulate arachidonic acid metabolism in nonsmall cell lung cancer A549 cells by its inhibition of MAPKs and NF-kappaB signaling pathways; it can impair breast cancer cell invasion by suppressing nuclear factor-κB-dependent matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression.[3,4]
Pachymic acid has antioxidant activity, affects the removal effect of reactive oxygen species formation as did N-acetyl-L-cysteine and inhibits nuclear factor-κB translocation, it can mitigate the unfavorable conditions induced by AH Plus stimuli, therefore, the use of pachymic acid is suggested to prevent the complications of oral diseases such as inflammation and alveolar destruction of the oral cavity.[5]
Pachymic acid shows anti-inflammatory function and odontoblast differentiation via HO-1 pathway, suggests it may be applicable for prevention of oral inflammation or to improve dentin mineralization against several stresses.[6]
Pachymic acid has the sedative-hypnotic effects, can enhances pentobarbital-induced sleeping behaviors via GABAA-ergic systems in mice, it is proposed that PA may be useful for the treatment of sleep disturbed subjects with insomnia.[7]
Product
References
[1] Gapter L, Wang Z, Glinski J, et al. Biochem Bioph Res Co, 2005, 332(4):1153-61.
[2] Huang Y C, Chang W L, Huang S F, et al. Eur J Pharmacol, 2010, 648(1–3):39-49.[1]
[3] Ling H, Jia X, Zhang Y, et al. Mol Carcinogen, 2010, 49(3):271–82.
[4] Ling H, Zhang Y, Ng K Y, et al. Breast Cancer Res Tr, 2011, 126(3):609-20.
[5] Kim T G, Lee Y H, Lee N H, et al. J Endodont, 2013, 39(4):461-6.
[6] Lee Y H, Lee N H, Bhattarai G, et al. Oral Diseases, 2013, 19(2):193–9.
[7] Shah V K, Choi J J, Han J Y, et al. Biomol Ther, 2014, 22(2014):314-20.
[8] Duan Q, Yao L, Zhuang Y. Trad Chinese Drug Res Clin Pharmacol, 2010, 21(06):654-5.
Product Use Citation





