Natural Products
Ginsenoside Compound K
| Catalog No. | CFN99756 | 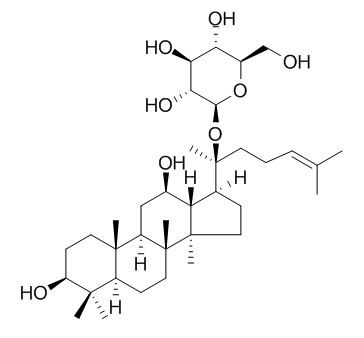 |
| CAS No. | 39262-14-1 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 622.88 | |
| Molecular Formula | C36H62O8 | |
| DBs | [PubChem]:274951195 [ChEMBL]:77146 [PCIDB]: |
Standard InChI:
InChI=1S/C36H62O8/c1-20(2)10-9-14-36(8,44-31-30(42)29(41)28(40)23(19-37)43-31)21-11-16-35(7)27(21)22(38)18-25-33(5)15-13-26(39)32(3,4)24(33)12-17-34(25,35)6/h10,21-31,37-42H,9,11-19H2,1-8H3/t21-,22+,23+,24-,25+,26-,27-,28+,29-,30+,31-,33-,34+,35+,36-/m0/s1
Biological Activity
Ginsenoside compound K (C-K) is a metabolite of the protopanaxadiol-type saponins of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer (Araliaceae), has long been used to treat against the development of cancer, inflammation, allergies, and diabetes; C-K acts as a unique HUVEC migration inhibitor by regulating MMP expression, as well as the activity of SPHK1 and its related sphingolipid metabolites.[1]
Ginsenoside compound K, the intestinal metabolite of ginseng saponin, has various chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic activities, including anti-tumor activity; C-K suppresses the activation of the NF-κB pathway, may become a potential cytotoxic drug in the prevention and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma( HCC).[2]
Ginsenoside compound K shows significant anti-proliferative effects and pro
-apoptotic effects in HCT-116 and SW-480 cells at concentrations of 30-50 uM, suggests that C-K could be potentially effective anti-colorectal cancer agent.[3]
Ginsenoside CK has anti-cancer effect on NPC cells, C-K-induced apoptosis of HK-1 cells was mediated by the mitochondrial pathway and could significantly inhibit tumor growth in vivo.[4]
Product
Official website: Ginsenoside Compound K
Japanese website: Ginsenoside Compound K
Chinese website: Ginsenoside Compound K
Japanese website: Ginsenoside Compound K
Chinese website: Ginsenoside Compound K
References
[1] Shin K O, Seo C H, Cho H H, et al. Arch Pharm Res, 2014, 37(9):1183-92.
[2] Ming Y, Chen Z, Chen L, et al.Planta Med, 2011, 77(5):428-33.
[3] Wang C Z, Du G J, Zhang Z, et al.Int J Oncol , 2012, 40(6):1970-6.
[4] Law K M, Kwok H H, Poon P Y, et al. Chinese Medicine, 2014, 9(1):1-9.
[5] Zhou W, Luo Z S, Zhou P, et al. Chromatogram, 2005, 23(3):270-2.
Product Use Citation





