Natural Products
Hydroxysafflor yellow A
| Catalog No. | CFN99950 | 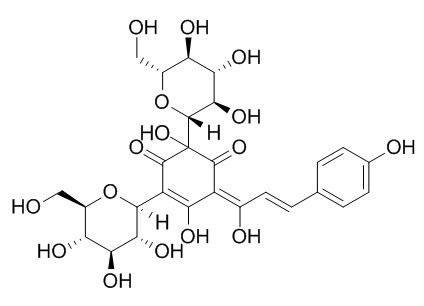 |
| CAS No. | 78281-02-4 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 612.53 | |
| Molecular Formula | C27H32O16 | |
| DBs | [PubChem]:274951004 [ChEMBL]: [PCIDB]:24213 |
Standard InChI:
InChI=1S/C27H32O16/c28-7-12-16(32)19(35)21(37)23(42-12)15-18(34)14(11(31)6-3-9-1-4-10(30)5-2-9)24(39)27(41,25(15)40)26-22(38)20(36)17(33)13(8-29)43-26/h1-6,12-13,16-17,19-23,26,28-30,32-33,35-41H,7-8H2/b6-3+/t12?,13?,16-,17-,19?,20?,21+,22+,23+,26-,27?/m1/s1
Biological Activity
Hydroxysafflor yellow A (HSYA), isolated from the dried flower of Carthamus tinctorius L. , which is extensively used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat cirrhosis, can protect against chronic carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis, might be a promising antifibrotic agent in chronic liver disease.[1]
Hydroxysafflor yellow A can provide protection to H9c2 cardiomyocytes against A/R-induced apoptosis, and this protective effect largely depends on the upregulation of HO-1 expression through the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 signaling pathway.[2]
Hydroxysafflor yellow A may provide neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia/
reperfusion injury through its suppression of inflammatory responses following focal ischemia reperfusion, and its antioxidant action by inhibiting the opening of mtPTP by a free radical scavenging action in the brain.[3-5]
Hydroxysafflor yellow A could enhance the survival of ECs under hypoxia, which may be correlated with its effect of upregulating the bcl-2/bax ratio and promoting HIF-1 alpha protein accumulation, which increases VEGF, these findings provide evidence for the mechanisms by which HSYA maintains EC survival under hypoxia.[6]
Hydroxysafflor yellow A suppresses inflammatory responses of BV2 microglia after oxygen-glucose deprivation, which is probably associated with the inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway and phosphorylation of p38.[7]
Product
Official website: Hydroxysafflor yellow A
Japanese website: Hydroxysafflor yellow A
Chinese website: Hydroxysafflor yellow A
Japanese website: Hydroxysafflor yellow A
Chinese website: Hydroxysafflor yellow A
References
[1] Zhang Y, Guo J, Dong H, et al. Eur J Pharmacol, 2011, 660(2–3):438-44.
[2] Liu S X, Zhang Y, Wang Y F, et al. Int J Cardiol, 2012, 160(2):95-101.
[3] Wei X, Liu H, Sun X, et al. Neurosci Lett, 2005, 386(1):58-62.
[4] Tian J, Li G, Liu Z, et al. Pharmacology, 2008, 82(2):121-6.
[5] Ye S Y, Gao W Y. Arch Pharml Res, 2008, 31(8):1010-5.
[6] Ji D B, Zhu M C, Zhu B, et al. J Cardiovasc Pharm, 2008, 52(2):191-202.
[7] Li J. Neurosci Lett, 2013, 535(1):51-6.
[8]Tan S J, Chi J P, He Y Q, et al. Pharm J Chinese Peoples Liberation Army, 2013(05):464-5.
Product Use Citation





