Natural Products
Arctiin
| Catalog No. | CFN99991 | 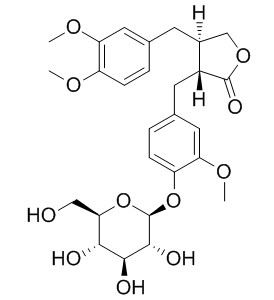 |
| CAS No. | 20362-31-6 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 534.55 | |
| Molecular Formula | C27H34O11 | |
| DBs | [PubChem]:274950963 [ChEMBL]:80793 [PCIDB]:646 |
Standard InChI:
InChI=1S/C27H34O11/c1-33-18-6-4-14(10-20(18)34-2)8-16-13-36-26(32)17(16)9-15-5-7-19(21(11-15)35-3)37-27-25(31)24(30)23(29)22(12-28)38-27/h4-7,10-11,16-17,22-25,27-31H,8-9,12-13H2,1-3H3/t16-,17+,22?,23+,24-,25?,27+/m0/s1
Biological Activity
Arctiin, a lignan isolated from Arctium lappa (burdock) seeds, has a protective effect on 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine (PhIP) -induced carcinogenesis particularly in the mammary gland in the promotion period, it may have a weak co-carcinogenic influence on MeIQx-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. [1]
Arctiin has been reported to have anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, antibacterial, and antiviral effects in vitro, it may exert anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting the pro-inflammatory mediators through the inactivation of NF-kB.[2]
Arctiin significantly induces cell detachment and decreases the cell numbers via the up-regulation of MUC-1 mRNA and protein in PC-3 cells.[3]
Arctiin down-regulates cyclin D1 protein expression and that this at least partially contributes to the anti-proliferative effect of arctiin.[4]
Arctiin has ameliorative effects on glomerulonephritis is carried out mainly by suppression of NF-κB activation and nuclear translocation and the decreases in the levels of these pro-inflammatory cytokines, while SOD is involved in the inhibitory pathway of NF-κB activation; arctiin has favorable potency for the development of an inhibitory agent of NF-κB and further application to clinical treatment of glomerulonephritis, though clinical studies are required.[5]
Arctiin induces an UVB protective effect in human dermal fibroblast cells through microRNA expression changes.[6]
Arctigenin and arctiin have antiproliferative effect.[7]
Product
References
[1] Hirose M, Yamaguchi T, Cui L, et al. Cancer Lett, 2000, 155(1):79-88.
[2] Lee S, Shin S, Kim H, et al. J Inflamm, 2010, 8(1):321-4.
[3] Huang D M, Guh J H, Chueh S C, et al. Prostate, 2004, 59(3):260-7.
[4] Matsuzaki Y, Koyama M, Hitomi T, et al. Oncol Rep, 2008, 19(3):721-7.
[5] Wu J G, Wu J Z, Sun L N, et al. Phytomed Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol, 2009, 16(11):1033-41.
[6] Lee G T, Cha H J, Lee K S, et al. Int J Mole Med, 2014, 33(3):640-8.
[7] Shi Y R, Ahn J W, Kang Y H, et al. Arch Pharml Res, 1995, 18(6):462-3.
[8] Zheng L, Song Y. Pharm Clin Chinese Mat Med, 2011, 02(2):23-6.
Product Use Citation





