| Description: |
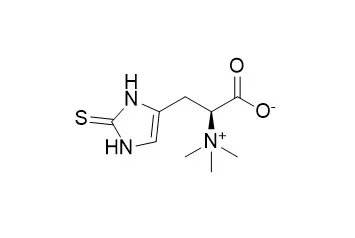
Ergothioneine is synthesized by certain bacteria and fungi. It is generally considered an antioxidant, but also has anti-inflammatory, cyto-protective, liver-protecting properties. |
| In vitro: |
| Free Radic Biol Med . 2019 Apr;134:498-504. | | Regeneration of ergothioneine after reaction with singlet oxygen[Pubmed: 30721726] | | Ergothioneine (ET), an imidazole-2-thione derivative of histidine betaine, is generally considered an antioxidant. Important antioxidants are typically regenerated from their oxidized products, to prevent the interceptors from being lost after a single chemical reaction with a reactive oxygen species. However, no mechanism for the complete regeneration of ET has yet been uncovered. Here we define a non-enzymatic multi-step cycle for the regeneration of ET after reaction with singlet oxygen (1O2). All reaction steps were verified by density functional theory computations. Four molecules of GSH are used per turn to detoxify 1O2 to water. Pure 1O2 was generated by thermolysis at 37 °C of the endoperoxide DHPNO2. Addition of 1 mM ET to 10 mM DHPNO2 and 10 mM GSH increased the production of oxidized GSH (GSSG), measured by LC-MS/MS, by a factor of 26 (water) and 28 (D2O), respectively. In the same assay, the ring of ET alone was able to drive the cycle at equal speed; thus, the zwitterionic amino acid backbone was not involved. Our data suggest that ET reacts at least 4-fold faster with 1O2 than ascorbic acid. ET must now be viewed as tightly linked with the GSH/GSSG redox couple. The necessary thiol foundation is present in all mammalian and vertebrate cells, and also in all species that generate ET, such as cyanobacteria, mycobacteria, and fungi. Regeneration provides a decisive advantage for ET over other reactive, but non-recoverable, compounds. Our findings substantiate the importance of ET for the eradication of noxious 1O2. | | Can J Physiol Pharmacol . 2021 Nov;99(11):1137-1147. | | L-ergothioneine and metformin alleviates liver injury in experimental type-2 diabetic rats via reduction of oxidative stress, inflammation, and hypertriglyceridemia[Pubmed: 34582252] | | Type-2 diabetes (T2D) is associated with liver toxicity. L-ergothioneine (L-egt) has been reported to reduce toxicity in tissues exposed to injury, while metformin is commonly prescribed to manage T2D. Hence, this study evaluates the hepatoprotective role of L-egt, with or without metformin, in T2D male rats. A total of 36 adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into non-diabetic (n = 12) and diabetic (n = 24) groups. After induction of diabetes, animals were divided into six groups (n = 6) and treated orally either with deionized water, L-egt (35 mg/kg bodyweight (bwt)), metformin (500 mg/kg bwt), or a combination of L-egt and metformin for 7 weeks. Body weight and blood glucose were monitored during the experiment. Thereafter, animals were euthanized and liver tissue was excised for biochemical, ELISA, real-time quantitative PCR, and histopathological analysis. L-egt with or without metformin reduced liver hypertrophy, liver injury, triglycerides, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Also, L-egt normalized mRNA expression of SREBP-1c, fatty acid synthase, nuclear factor kappa B, transforming growth factor β1, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2, and sirtuin-1 in diabetic rats. Furthermore, co-administration of L-egt with metformin to diabetic rats reduced blood glucose and insulin resistance. These results provide support to the therapeutic benefits of L-egt in the management of liver complications associated with T2D. | | Zygote . 2018 Apr;26(2):149-161. | | l-Ergothioneine improves the developmental potential of in vitro sheep embryos without influencing OCTN1-mediated cross-membrane transcript expression[Pubmed: 29607799] | | SummaryThe objective of the study was to investigate the effect of l-ergothioneine (l-erg) (5 mM or 10 mM) supplementation in maturation medium on the developmental potential and OCTN1-dependant l-erg-mediated (10 mM) change in mRNA abundance of apoptotic (Bcl2, Bax, Casp3 and PCNA) and antioxidant (GPx, SOD1, SOD2 and CAT) genes in sheep oocytes and developmental stages of embryos produced in vitro. Oocytes matured with l-erg (10 mM) reduced their embryo toxicity by decreasing intracellular ROS and increasing intracellular GSH in matured oocytes that in turn improved developmental potential, resulting in significantly (P < 0.05) higher percentages of cleavage (53.72% vs 38.86, 46.56%), morulae (34.36% vs 20.62, 25.84%) and blastocysts (14.83% vs 6.98, 9.26%) compared with other lower concentrations (0 mM and 5 mM) of l-erg without change in maturation rate. l-Erg (10 mM) treatment did not influence the mRNA abundance of the majority of apoptotic and antioxidant genes studied in the matured oocytes and developmental stages of embryo. A gene expression study found that the SLC22A4 gene that encodes OCTN1, an integral membrane protein and specific transporter of l-erg was not expressed in oocytes and developmental stages of embryos. Therefore it was concluded from the study that although there was improvement in the developmental potential of sheep embryos by l-erg supplementation in maturation medium, there was no change in the expression of the majority of the genes studied due to the absence of the SLC22A4 gene in oocytes and embryos that encode OCTN1, which is responsible for transportation of l-erg across the membrane to alter gene expression. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Antioxidants (Basel) . 2021 Sep 7;10(9):1424. | | S-Methyl-L-Ergothioneine to L-Ergothioneine Ratio in Urine Is a Marker of Cystine Lithiasis in a Cystinuria Mouse Model[Pubmed: 34573056] | | Cystinuria, a rare inherited aminoaciduria condition, is characterized by the hyperexcretion of cystine, ornithine, lysine, and arginine. Its main clinical manifestation is cystine stone formation in the urinary tract, being responsible for 1-2% total and 6-8% pediatric lithiasis. Cystinuria patients suffer from recurrent lithiasic episodes that might end in surgical interventions, progressive renal functional deterioration, and kidney loss. Cystinuria is monitored for the presence of urinary cystine stones by crystalluria, imaging techniques or urinary cystine capacity; all with limited predicting capabilities. We analyzed blood and urine levels of the natural antioxidant L-ergothioneine in a Type B cystinuria mouse model, and urine levels of its metabolic product S-methyl-L-ergothioneine, in both male and female mice at two different ages and with different lithiasic phenotype. Urinary levels of S-methyl-L-ergothioneine showed differences related to age, gender and lithiasic phenotype. Once normalized by L-ergothioneine to account for interindividual differences, the S-methyl-L-ergothioneine to L-ergothioneine urinary ratio discriminated between cystine lithiasic phenotypes. Urine S-methyl-L-ergothioneine to L-ergothioneine ratio could be easily determined in urine and, as being capable of discriminating between cystine lithiasis phenotypes, it could be used as a lithiasis biomarker in cystinuria patient management. | | PLoS One . 2020 Mar 31;15(3):e0230977. | | Effect of L-Ergothioneine on the metabolic plasma profile of the RUPP rat model of pre-eclampsia[Pubmed: 32231385] | | Introduction: Pre-eclampsia is a major cause of maternal and fetal mortality and morbidity worldwide. Its pathophysiology remains unclear, but mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress have been implicated. L-Ergothioneine is a naturally occurring, water-soluble betaine, that has demonstrated antioxidant properties. Using the reduced uterine perfusion pressure (RUPP) rat model of pre-eclampsia, this study aimed to define the plasma metabolic profile following treatment with L-Ergothioneine.
Methods: The effect of L-Ergothioneine (ET) treatment was explored using in vivo treatment in rats: Sham control (SC, n = 5), RUPP control (RC, n = 5), Sham +ET (ST, n = 5), RUPP +ET (RT, n = 5). Differential expression of plasma metabolites were obtained using untargeted liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Statistical analysis was performed on normalised data comparing RC to SC, RT to RC, and RT to ST. Metabolites significantly altered (FDR < 0.05) were identified through database search.
Results: We report significantly lower levels of L-palmitoylcarnitine in RC compared to SC, a fatty acyl substrate involved in beta-oxidation in the mitochondria. We report that a metabolite that has been associated with oxidative stress (Glutamylcysteine) was detected at significantly higher levels in RT vs RC and RT vs ST. Five metabolites associated with inflammation were significantly lower in RT vs RC and three metabolites in RT vs ST, demonstrating the anti-inflammatory effects of ET in the RUPP rat model of pre-eclampsia.
Conclusions: L-Ergothioneine may help preserve mitochondrial function by increasing antioxidant levels, and reducing inflammatory responses associated with pre-eclampsia. This study shows the potential of L-Ergothioneine as a treatment for pre-eclampsia. | | Life Sci . 2018 Aug 15;207:516-524. | | Ergothioneine ameliorates oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy in rats[Pubmed: 29981320] | | Aims: Oxaliplatin (l-OHP) is a key drug in therapeutic regimens for metastatic or advanced-stage colorectal cancer, but causes peripheral neuropathy as a dose-limiting adverse effect. It is reported that this peripheral neuropathy results from l-OHP accumulation in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons, and that one of the transporters responsible for the accumulation in DRG neurons is organic cation transporter novel (OCTN) 1. Here, we examined whether co-administration of ergothioneine, a substrate/inhibitor of OCTN1, with l-OHP could prevent this peripheral neuropathy.
Main methods: l-OHP (4 mg/kg, i.p., twice/week, for 6 weeks) and ergothioneine or l-carnitine (1.5 or 15 mg/kg, i.v., twice per l-OHP administration) were administered to rats, and tissue/cellular platinum concentrations and peripheral neuropathy were determined. Expression of transporters in DRG neuronal cells was evaluated by real-time PCR and immunocytochemistry.
Key findings: On administration of l-OHP to rats, it accumulated in DRG neurons and their mitochondria, while negligible accumulation was found in Schwann cells. Expression of OCTN1 was observed in DRG neurons, especially in small- and medium-sized ones, which are responsible for the nociceptive response. In rats repeatedly administered l-OHP, co-administration of ergothioneine (15 mg/kg), but not l-carnitine, a substrate/inhibitor of OCTN2, decreased l-OHP accumulation in DRGs and development of the mechanical allodynia.
Significance: These results indicated that l-OHP-induced peripheral neuropathy was ameliorated by co-administration of ergothioneine, at least in part, via a decrease in its accumulation in DRG neurons. Plant diets contain ergothioneine, and thus their consumption might offer relief to patients suffering from l-OHP-induced peripheral neuropathy. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)