| Structure Identification: |
| Chinese Traditional & Herbal Drugs,2014 ,45 (14):1984-8. | | Chemical constituents from Scilla scilloides[Reference: WebLink] | To study the chemical constituents from Scilla scilloides.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The chemical constituents were isolated and purified by column chromatography and their structures were identified by spectral data. Eighteen compounds were isolated from S. scilloides. Their structures were identified as scillascillin(1), 2-hydroxy-7-O-methylscillascillin(2), 4′-demethyleucomin(3), 5-hydroxy-7-methoxy-3-(4-hydroxybenzylidene) chroman-4-one(4), 4′-demethyl-3, 9-dihydroeucomin(5), 3′-hydroxy-3, 9-dihydroeucomin(6), 8-O-demethyl-7-O-methyl-3, 9-dihydropunctatin(7), apigenin(8), luteolin(9), chrysoeriol(10), 3-dehydro-15-deoxoeucosterol(11), 15-deoxoeucosterol(12), 4-allylpyrocatechol(13), norlichexanthone(14), Drimiopsin C(15), 6-feruloylcatalpol(16), catalposide(17), and specioside(18).
CONCLUSIONS:
Iridoids(16—18) are isolated from the genus Scilla L. for the first time. Compounds 4, 7—10, and 13—18 are isolated from the plants of this genus for the first time. | | J Nat Prod. 2004 Oct;67(10):1726-8. | | Xanthones from Drimiopsis maculata.[Pubmed: 15497949 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
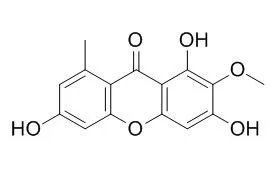
Six new xanthones, drimiopsin A, drimiopsin B, Drimiopsin C, drimiopsin D, drimiopsin E, drimiopsin F , have been isolated from the South African Drimiopsis maculata.
CONCLUSIONS:
The structures of these compounds were difficult to elucidate due to the lack of correlating protons seen in the NMR spectra, and INADEQUATE spectra were used to confirm the structures. Xanthones have not previously been reported from the Hyacinthaceae. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)