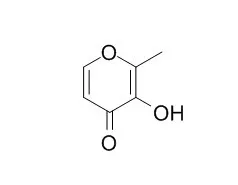
Maltol (3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4-pyrone), formed by the thermal degradation of starch, is found in coffee, caramelized foods, and Korean ginseng root. This study investigated whether Maltol could rescue neuroretinal cells from oxidative injury in vitro.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
R28 cells, which are rat embryonic precursor neuroretinal cells, were exposed to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2, 0.0 to 1.5 mM) as an oxidative stress with or without Maltol (0.0 to 1.0 mM). Cell viability was monitored with the lactate dehydrogenase assay and apoptosis was examined by the terminal deoxynucleotide transferase-mediated terminal uridine deoxynucleotidyl transferase nick end-labeling (TUNEL) method. To investigate the neuroprotective mechanism of Maltol, the expression and phosphorylation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and p38 were evaluated by Western immunoblot analysis. R28 cells exposed to H2O2 were found to have decreased viability in a dose- and time-dependent manner. However, H2O2-induced cytotoxicity was decreased with the addition of Maltol. When R28 cells were exposed to 1.0 mM H2O2 for 24 hours, the cytotoxicity was 60.69 ± 5.71%. However, the cytotoxicity was reduced in the presence of 1.0 mM Maltol. This H2O2-induced cytotoxicity caused apoptosis of R28 cells, characterized by DNA fragmentation. Apoptosis of oxidatively-stressed R28 cells with 1.0 mM H2O2 was decreased with 1.0 mM Maltol, as determined by the TUNEL method. Western blot analysis showed that treatment with Maltol reduced phosphorylation of NF-κB, ERK, and JNK, but not p38. The neuroprotective effects of Maltol seemed to be related to attenuated expression of NF-κB, ERK, and JNK.
CONCLUSIONS:
Maltol not only increased cell viability but also attenuated DNA fragmentation. The results obtained here show that Maltol has neuroprotective effects against hypoxia-induced neuroretinal cell damage in R28 cells, and its effects may act through the NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways. |





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)