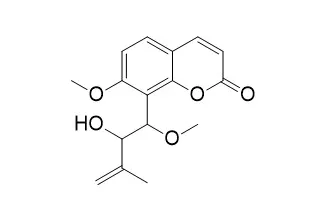
| Structure Identification: |
| Biol Pharm Bull . 2014;37(4):694-697. | | Vasorelaxing activity of two coumarins from Murraya paniculata leaves[Pubmed: 24694618] | | In the search for novel chemical scaffolds leading to potential antihypertensive agents, the methanol extract of Murraya paniculata leaves was assessed for its effects on isolated rat aorta rings. The vasorelaxing effect of the chloroform fraction of the methanol plant extract was the most potent for its vasorelaxing activity on rat aorta rings contracted by 60 mM K(+) (K60). Two coumarins were isolated from the chloroform fraction: the novel kimcuongin (1) and the known Murracarpin (2). Their structures were determined from spectroscopic evidences including (1)H- and (13)C-NMR, correlation spectroscopy (COSY), nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy (NOESY), heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC), heteronuclear single quantum correlation (HSQC), and high resolution mass spectrometry (HR-MS). Kimcuongin and, to a lesser extent, Murracarpin, showed vasorelaxing activity with IC50 values of 37.7 μM and 139.3 μM, respectively. The coumarins kimcuongin and Murracarpin may thus represent a novel class of vasodilators of natural source. | | Pharm Biol. 2010 Dec;48(12):1344-1353. | | Evaluation of anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities of Murraya exotica[Pubmed: 20738224] | | Context: Leaves of Murraya exotica L. (Rutaceae) are used for the treatment of various disorders such as cough, fever, and infectious wounds, as well as alleviating pains in folk medicine in southern China.
Objective: The objectives of this study were to investigate the in vivo antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of ethanol (70%) extracts and isolated compounds obtained from the dried leaves of M. exotica.
Materials and methods: The antinociceptive activities were evaluated with the methods of acetic acid-induced writhing response and hot-plate latent pain response test. Carrageenan induced hind paw edema, xylene induced ear edema, and a rat knee osteoarthritis model were employed to measure the anti-inflammatory activities. The compounds were isolated using column chromatography and thin-layer chromatography, and the structures identified by 1H NMR, 13C NMR, MS, and IR.
Results: The ethanol (70%) extracts significantly decreased in the acetic acid-induced writhing response; increased in hot-plate latency; suppressed xylene induced ear swelling and the carrageenan-induced paw edema effectively. In the rat knee osteoarthritis model, the treatment of the ethanol (70%) extracts resulted in a significant increase in the activity of superoxide dismutase, an inhibition on inducible nitric oxide synthase activity, and a decrease in the contents of interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α of the rat serum. Following this, we explored the components of the ethanol (70%) extracts and isolated six known coumarins, including Murracarpin, which exhibited the most potential in antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities.
Discussion and conclusion: M. exotica displayed remarkable antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)