| Description: |
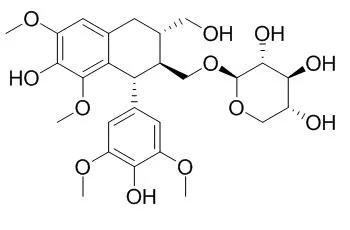
Nudiposide has significant neuroprotective activities against glutamate-injured neurotoxicity in HT22 cells. It also exhibits protective effect against sepsis in a mouse model and can decrease the plasma levels of TNF-α, IL-10 and ALT activity.
|
| Targets: |
TNF-α | IL Receptor | ALT |
| In vitro: |
| Pharmacogn Mag. 2015 Oct;11(Suppl 2):S303-7. | | Neuroprotective compounds of Tilia amurensis.[Pubmed: 26664019] | In this study, we isolated five compounds from T. amurensis and determined whether protected neuronal cells against glutamate-induced oxidative stress in HT22 cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Compounds were isolated using chromatographic techniques including silica gel, Sephadex LH-20 open column and high performance liquid chromatography analysis, and evaluated neuroprotective effect in HT22 cells by 3-(4,5-dimethythiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide assay. RESULTS: β-D-fructofuranosyl α-D-glucopyranoside (1), (-)-epicatechin (2), Nudiposide (3), lyoniside (4), and scopoletin (5) were isolated by bioactivity-guided fractionation from the ethyl acetate fraction of T. amurensis. Among them, (-)-epicatechin, Nudiposide, lyoniside, and scopoletin had significant neuroprotective activities against glutamate-injured neurotoxicity in HT22 cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results demonstrated that compound two, three, four, and five have a pronounced protective effect against glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in HT22 cells. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Arch Pharm Res. 2011 Sep;34(9):1443-50. | | Protective constituents against sepsis in mice from the root barks of Ulmus davidiana var. japonica.[Pubmed: 21975805 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the course of isolating preventive agents against sepsis based on the in vivo assay model, eleven known compounds, (-)-catechin (1), catechin-7-O-β-apiofuranoside (2), catechin-7-O-α-Lrhamnopyranoside (3), catechin-3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside (4), catechin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (5), butyl (+)-5'-methoxyisolariciresinol-9'-O-β-D-xylopyranoside (6), lyoniside (7), Nudiposide (8), α-nigerose (9), butyl α-D-fructofuranoside (10), and procyanidin B(3) (11) were isolated from the root barks of Ulmus davidiana var. japonica.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 2, 6, and 8 significantly protected against sepsis in a mouse model with survival rates of mice exposed to 10 mg/kg of LPS/D-GalN ranged from 80%-100%. Among them, 8 exhibited the most potent protective effect and decreased the plasma levels of TNF-α, IL-10 and ALT activity. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)