| Structure Identification: |
| J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 May 23;236:31-41. | | Exploring on the bioactive markers of Codonopsis Radix by correlation analysis between chemical constituents and pharmacological effects.[Pubmed: 30776470] | Codonopsis Radix is a commonly used traditional Chinese medicine, and has the effect of strengthening spleen and tonifying lung, nourishing blood and engendering liquid. In addition, it is also used as important food materials.
The aim of the study was to explain the underlying correlations between chemical constituents and pharmacological effects and explore the bioactive markers of Codonopsis Radix.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Codonopsis Radix samples from Min county, Gansu province processed with different methods were taken as the materials, UPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS/MS analysis was conducted to identify the compounds and establish UPLC fingerprint. Meanwhile, hematopoietic and immunologic functions of Codonopsis Radix were investigated to obtain relevant pharmacological index. Then, the correlation analysis between chemical constituents in UPLC fingerprints and pharmacological effects was carried out. The plant name was confirmed to the database "The Plant List" (www.theplantlist.org).
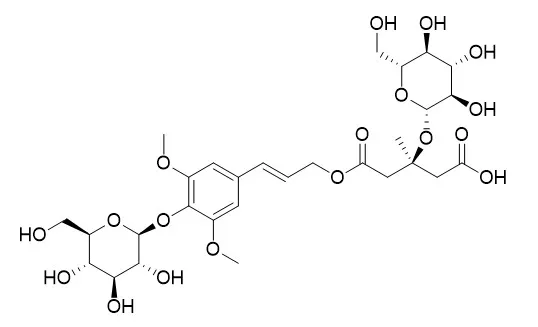
According to the results of canonical correlation analysis, tryptophan, syringin, Tangshenoside I, codonopyrrolidium A, lobetyolin and two unknown compounds might be the potential bioactive markers related to the hematopoietic and immunologic functions of Codonopsis Radix, which could be recommended as the index compounds.
CONCLUSIONS:
This study illustrated the underlying correlations between chemical constituents and pharmacological effects, explored the pharmacological material basis, and could lay a foundation for the improvement of quality standard of Codonopsis Radix. | | Agricultural Chemistry & Biotechnology, 2006, 49(4):162-164. | | α-Glucosidase Inhibitors from the Roots of Codonopsis lanceolata Trautv.[Reference: WebLink] | Codonopsis lanceolata Trautv. is a plant of the Campanulaceae family, which is distributed throughout Korea, Japan and China. C. lanceolata has been cultivated and its roots have been used as food especially in Korea. Other Codonopsis species, C. pilosula and C. tangshen were used as medicine (Tang-Sam) for ulcers, memory improvement and immunostimulating; however, C. lanceolata was treated as an adulterant in Japan and China.1,2).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Several studies of the chemical constituents of C. pilosula, C. tangshen and C. ussuriensis have been reported in the literatures.3-6) There are some reports on secondary metabolites of C. lanceolata; on the isolation of triterpenoid, saponin and alkaloid from the roots7-10) and the isolation of flavonoids from the leaves.11).
CONCLUSIONS:
The present report deals with the isolation, structure determination and α-glucosidase inhibition activity of Tangshenoside I and adeonsine from the roots of C. lanceolata. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)