| Structure Identification: |
| Journal of Food Measurement & Characterization, 2018,29(5)808–819. | | HPLC-ESI-MS/MS characterization of phenolics in prunus amygdalus, cultivar “umm alfahm” and its antioxidant and hepatoprotective activity.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
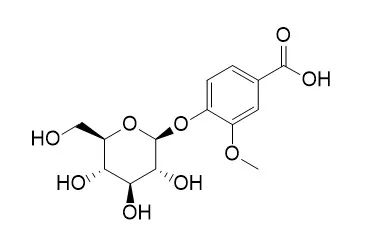
Metabolite profiling of the total ethanolic extract of Prunus amygdalus stem and leaves was carried out for the first time using LC-DAD-ESI-MS in the negative ion mode to investigate its chemical composition. Results revealed the identification of 33 phenolic compounds.
Fifteen compounds were investigated in P. amygdalus for the first time and identified as; veratic acid, rosmarinicacid, protocatechuic acid-hexoside, 3-O-caffeoylquinic acid (neochlorogenic acid), dihydroquercetin- hexoside, coumaroyl-quinic acid, Vanillic acid glucoside, cis piceid, hesperidin, dihydrokaempferol, acteoside, quercetin acetyl hexoside, homovanillic acid, fisetin-deoxyhexoside. The antioxidant potential of the total ethanolic extract (EE) and the fractions: petroleum ether (PE), chloroform (CE), ethyl acetate (EtE), methanol eluted diaion (DME) and diaion eluted with 50% methanol (D 50%E) was performed using DPPH assay. The most potent antioxidant EE, EtE and D50%E extracts (compared with vitamin C) were selected for further hepatoprotective assessment against hepatotoxicity induced by thioacetamide in a dose of 200 mg/kg compared with silymarin (50 mg/kg) as a standard drug.
CONCLUSIONS:
Results revealed the significant reversal of the deleterious effects of thioacetamide on serum ALT, AST and total protein in the order: EtE > (Silymarin = EE) > D50% E. The biochemical results were corroborated with the histological studies of liver. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)