| Description: |
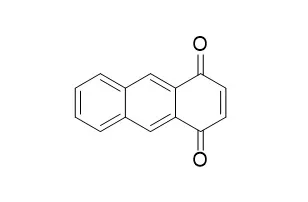
1,4-Anthraquinone is an anticancer drug that blocks nucleoside transport, inhibits macromolecule synthesis, induces DNA fragmentation, and decreases the growth and viability of L1210 leukemic cells in the same nanomolar range as daunorubicin in vitro.1,4-Anthraquinone is proposed as a novel pre-column reagent for high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) determination of N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and captopril (CAP) in pharmaceutical formulations. |
| In vitro: |
| Anti Cancer Drugs, 2000, 11(5):339-352. | | 1,4-Anthraquinone: an anticancer drug that blocks nucleoside transport, inhibits macromolecule synthesis, induces DNA fragmentation, and decreases the growth and viability of L1210 leukemic cells in the same nanomolar range as daunorubicin in vitro.[Reference: WebLink] | 1,4-Anthraquinone (AQ) was synthesized and shown to prevent L1210 leukemic cells from synthesizing macromolecules and growing in vitro. In contrast, its dihydroxy-9,10anthraquinone precursor, quinizarin, was inactive.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The antitumor activity of AQ was compared to that of daunorubicin (DAU), which is structurally different from AQ but also contains a quinone moiety. AQ is equipotent to DAU against L1210 tumor cell proliferation (IC50: 25 nM at day 2 and 9 nM at day 4) and viability (IC50: 100 nM at day 2 and 25 nM at day 4), suggesting that its cytostatic and cytotoxic activities are a combination of drug concentration and duration of drug exposure. Since AQ does not increase but rather decreases the mitotic index of L1210 cells at 24 h, it is not an antitubulin drug but might arrest early stages of cell cycle progression. Like DAU, a 1.5-3 h pretreatment with AQ is sufficient to inhibit the rates of DNA, RNA and protein syntheses (IC50: 2 microM) determined over 30-60 min periods of pulse-labeling in L1210 cells in vitro. In contrast to DAU, which is inactive, a 15 min pretreatment with AQ has the advantage of also inhibiting the cellular transport of both purine and pyrimidine nucleosides (IC50: 2.5 microM) over a 30 s period in vitro. Hence, AQ may prevent the incorporation [3H]thymidine into DNA because it rapidly blocks the uptake of these nucleosides by the tumor cells. After 24 h, AQ induces as much DNA cleavage as camptothecin and DAU, two anticancer drugs producing DNA strand breaks and known to, respectively, inhibit topoisomerase I and II activities. However, the concentration-dependent induction of DNA cleavage by AQ, which peaks at 1.6-4 microM and disappears at 10-25 microM, resembles that of DAU. The mechanism by which AQ induces DNA cleavage is inhibited by actinomycin D, cycloheximide and aurintricarboxylic acid, suggesting that AQ activates endonucleases and triggers apoptosis.
The abilities of AQ to block nucleoside transport, inhibit DNA synthesis and induce DNA fragmentation are irreversible upon drug removal, suggesting that this compound may rapidly interact with various molecular targets in cell membranes and nuclei to disrupt the functions of nucleoside transporters and nucleic acids, and trigger long-lasting antitumor effects which persist after cessation of drug treatment.
CONCLUSIONS:
Because of its potency and dual effects on nucleoside transport and DNA cleavage, the use of bifunctional AQ with antileukemic activity in the nM range in vitro might provide a considerable advantage in polychemotherapy to potentiate the action of antimetabolites and sensitize multidrug-resistant tumor cells. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)