| Kinase Assay: |
| Chem Biol Interact. 1991;77(2):149-58. | | Effect of L-methionine on 2-carboxybenzaldehyde reductase induction by phenobarbital in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes.[Pubmed: 1991334] | Effects of phenobarbital (PB) and L-methionine on 2-Carboxybenzaldehyde (CBA) reductase in rat hepatocyte primary culture were examined.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Inclusion of PB in the culture medium markedly enhanced the CBA reductase activity while L-methionine, which elevates the cellular glutathione (GSH) level, suppressed the stimulatory effect of PB. This suppression, though less pronounced, was also found with other precursors of GSH biosynthesis. GSH-depletors, buthionine sulfoximine (BSO) or diethylmaleate (DEM), enhanced the CBA reductase activity suggesting that GSH plays an important role in enzyme induction. |
|
| Structure Identification: |
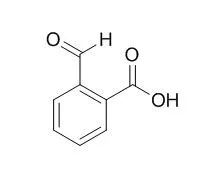
| Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2014 Aug 14;129:333-8. | | Synthesis, spectroscopic, anticancer and antibacterial studies of Ni(II) and Cu(II) complexes with 2-carboxybenzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone.[Pubmed: 24747857] | | Ni(II) and Cu(II) complexes of 2-Carboxybenzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone (L) were synthesized and investigated by their spectral and analytical data. These newly synthesized complexes have a composition of M(L)X(H2O)2 (where M=Ni(II), Cu(II) and X=Cl(-), NO3(-), CH3COO(-)) and (L) is the tridentate Schiff base ligand. The ligand and its complexes have been characterized on the basis of analytical, molar conductivity, magnetic susceptibility measurements, FT-IR, ESR, (1)H NMR and electronic spectral analysis. | | Biochem J. 1998 May 15;332 ( Pt 1):21-34. | | Molecular cloning, expression and catalytic activity of a human AKR7 member of the aldo-keto reductase superfamily: evidence that the major 2-carboxybenzaldehyde reductase from human liver is a homologue of rat aflatoxin B1-aldehyde reductase.[Pubmed: 9576847] | The masking of charged amino or carboxy groups by N-phthalidylation and O-phthalidylation has been used to improve the absorption of many drugs, including ampicillin and 5-fluorouracil. Following absorption of such prodrugs, the phthalidyl group is hydrolysed to release 2-Carboxybenzaldehyde (2-CBA) and the pharmaceutically active compound; in humans, 2-Carboxybenzaldehyde is further metabolized to 2-hydroxymethylbenzoic acid by reduction of the aldehyde group.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present work, the enzyme responsible for the reduction of 2-Carboxybenzaldehyde in humans is identified as a homologue of rat aflatoxin B1-aldehyde reductase (rAFAR).In addition to reducing the dialdehydic form of aflatoxin B1-8,9-dihydrodiol, hAFAR shows high affinity for the gamma-aminobutyric acid metabolite succinic semialdehyde (SSA) which is structurally related to 2-Carboxybenzaldehyde, suggesting that hAFAR could function as both a SSA reductase and a 2-Carboxybenzaldehyde reductase in vivo.
CONCLUSIONS:
This hypothesis is supported in part by the finding that the major peak of 2-Carboxybenzaldehyde reductase activity in human liver co-purifies with hAFAR protein. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)