| In vitro: |
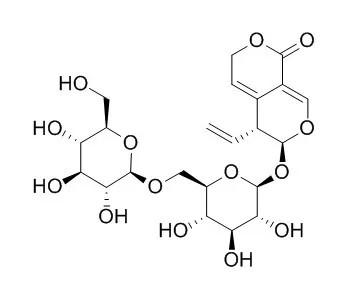
| Phytother Res. 2012 Feb;26(2):168-73. | | Inhibitory effects of secoiridoids from the roots of Gentiana straminea on stimulus-induced superoxide generation, phosphorylation and translocation of cytosolic compounds to plasma membrane in human neutrophils.[Pubmed: 21584870] | Five secoiridoids, gentiopicroside (GTP), 6'-O-(2-hydroxy-3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-benzoyl)-sweroside (HGBS), 6'-O-beta-D-Glucosylgentiopicroside(GGTP), sweroside (SW) and swertiamarin (STM) were isolated from the roots of G. straminea.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The effect of these secoiridoids on stimulus-induced superoxide generation in human neutrophils was assayed by measuring the reduction of ferricytochrome c. Tyrosyl or serine/threonine phosphorylation of neutrophil proteins, and translocation of the cytosolic compounds to the cell membrane were also investigated using specific monoclonal antibodies. The five secoiridoids used in the present experiment suppressed N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMLP)-induced superoxide generation in a concentration dependent manner. GTP and HGBS also suppressed phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and arachidonic acid (AA)-induced superoxide generation.
However, the other three secoiridoids showed no effect on PMA- and AA-induced superoxide generation.
CONCLUSIONS:
fMLP-, PMA- and AA-induced tyrosyl or serine/threonine phosphorylation and translocation of the cytosolic proteins to the cell membrane were suppressed in parallel with the suppression of the stimulus-induced superoxide generation. | | Phytochemistry, 1996, 42(5):1305-13. | | Acyl secoiridoids and antifungal constituents from Gentiana macrophylla.[Pubmed: 9397205] | LC-UV-mass spectrometry and bioassay co-directed fractionation of an aqueous acetone extract of the roots of Gentiana macrophylla gave three new chromene derivatives and two novel and six known secoiridoids, along with kurarinone, kushenol I, beta-sitosterol, stigmasterol, daucosterol, beta-sitosterol-3-O-gentiobioside, alpha-amyrin, oleanolic acid, isovitexin, gentiobiose and methyl 2-hydroxy-3-(1-beta-D-glucopyranosyl)oxybenzoate.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The structures of the new products were established from spectral and chemical evidence as 2-methoxyanofinic acid and macrophyllosides A-D. The six known secoiridoids were gentiopicroside, sweroside, 6'-O-beta-D-Glucosylgentiopicroside, 6'-O-beta-D-glucosylsweroside, trifloroside and rindoside. The new acid (2-methoxyanofinic acid), its methyl ester, kurarinone and kushenol I were shown to be active against the plant pathogenic fungus Cladosporium cucumerinum. The methyl ester and kurarinone inhibited also the growth of the human pathogenic yeast Candida albicans. Structure-activity relationships were studied. Thus, addition of a methoxyl group to the benzene nucleus of anofinic acid (2,2-dimethyl-2H-1-benzopyran-6-carboxylic acid) increased the antifungal activity remarkably whereas glycosylation at the carboxylic moiety was found to remove the activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
Esterification of the new acid induced its activity against C. albicans, but decreased its growth inhibition properties against C. cucumerinum. Hydroxylation of kurarinone at the 3 beta-position removed its activity against C. albicans and decreased the inhibition of C. cucumerinum. In addition, the chemotaxonomic significance of the identified constituents is discussed. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)