| Description: |
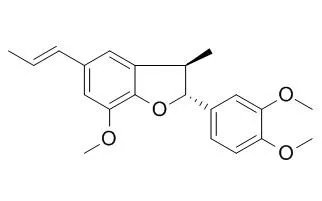
(-)-Acuminatin exerts hepatoprotective activities, perhaps by serving as a potent antioxidant. (+)-trans-Acuminatin, and (+)-cis-acuminatin show weak activity against platelet aggregation with IC50 values of 108.5 and 90.02 uM, respectively.(-)-Acuminatin, and machilin G show dose-dependent potent inhibitory activities against PLCgamma1 in vitro with IC50 values ranging from 8.8 to 26.0 microM, the inhibition of PLCgamma1 may be an important mechanism for an antiproliferative effect on the human cancer cells, therefore, these inhibitors may be utilized as cancer chemotherapeutic and chemopreventive agents. |
| In vitro: |
| J Pharm Pharmacol. 2000 Sep;52(9):1163-9. | | Antioxidant lignans from Machilus thunbergii protect CCl4-injured primary cultures of rat hepatocytes.[Pubmed: 11045899] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Eleven lignans (1-11) were isolated from the CH2Cl2 fraction of the bark of Machilus thunbergii Sieb. et Zucc. (Lauraceae). These were identified as (-)-Acuminatin (1), (-)-isoguaiacin (2), meso-dihydroguaiaretic acid (3), (+)-galbacin (4), (-)-sesamin (5), (+)-galbelgin (6), machilin A (7), machilin G (8), licarin A (9), and nectandrin A (10) and B (11). Primary cultures of rat hepatocytes were co-incubated for 90 min with the hepatotoxin CCl4 and each of the 11 lignans (50 microM). Hepatoprotective activity was determined by measuring the level of glutamic pyruvic transaminase released into the medium from the primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. (-)-Acuminatin, (-)-isoguaiacin and meso-dihydroguaiaretic acid all significantly reduced the level of glutamic pyruvic transaminase released. Further investigation revealed that these three compounds significantly preserved the levels and the activities of glutathione, superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase and catalase. (-)-Acuminatin, (-)-isoguaiacin and meso-dihydroguaiaretic acid also ameliorated lipid peroxidation as demonstrated by a reduction of malondialdehyde production.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that (-)-Acuminatin, (-)-isoguaiacin and meso-dihydroguaiaretic acid exert diverse hepatoprotective activities, perhaps by serving as potent antioxidants. | | Phytochemistry. 2016 Sep;129:36-44. | | Amides and neolignans from the aerial parts of Piper bonii[Pubmed: 27452451 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Six amides, piperbonamides A-F, three neolignans piperbonins A-C, and 11 known compounds were isolated from the aerial parts of Piper bonii (Piperaceae). The structures of piperbonamides A-F and piperbonins A-C were elucidated based on the analysis of 1D and 2D NMR and MS data.
CONCLUSIONS:
Piperbonin A, (+)-trans-Acuminatin, (+)-cis-Acuminatin, (+)-kadsurenone, and pipernonaline showed weak activity against platelet aggregation with IC50 values of 118.2, 108.5, 90.02, 107.3, and 116.3 μM, respectively, as compared with the positive control, tirofiban, with an IC50 value of 5.24 μM. Piperbonamides A-F were inactive against five tumor cell lines at concentrations up to 40 μM. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)