| In vitro: |
| Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Feb 1;276(2):390-5. | | Phytoalexin synthesis in soybean: purification and characterization of NADPH:2'-hydroxydaidzein oxidoreductase from elicitor-challenged soybean cell cultures.[Pubmed: 2306102] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
An NADPH:2'-Hydroxydaidzein oxidoreductase (HDR) from elicitor-challenged soybean cell cultures was purified to apparent homogeneity by a five-step procedure. The purification procedure included affinity adsorption on Blue Sepharose and elution of the enzyme with NADP+. It was shown by gel filtration and by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis that HDR consists of only one polypeptide, which has a Mr about 34,700. The pH optimum of the reaction was 7.0. Apparent Michaelis constants determined for 2'-Hydroxydaidzein, 2'-hydroxyformononetin, and NADPH were, respectively, 50, 60, and 56 microM. A low conversion of 2'-hydroxygenistein to the corresponding isoflavanone was also observed but isoflavones lacking a 2'-hydroxyl group and various other flavonoids did not serve as substrates.
CONCLUSIONS:
Enzymatically derived 2'-hydroxydihydrodaidzein gave a positive CD spectrum at 328 nm, which shows its 3R stereochemistry. Antibodies against HDR were raised in rats. | | Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2004, 14(22):1011-4. | | Anti-inflammatory flavonoids and pterocarpanoid from Crotalaria pallida and C. assamica.[Pubmed: 15013012] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
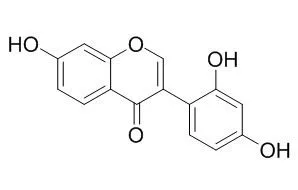
One new isoflavone, 5,7,4'-trihydroxy-2'-methoxyisoflavone (3) and seven, and four known compounds were isolated from the barks of Crotalaria pallida and the seeds of C. assamica, respectively.
The known compounds, apigenin (1) and 2'-hydroxygenistein (2), isolated from C. pallida, showed significant concentration-dependent inhibitory effects on the release of beta-glucuronidase and lysozyme from rat neutrophils in response to formyl-Met-Leu-Phe/cytochalasin B (fMLP/CB) with IC(50) values of 2.8+/-0.1 and 17.7+/-1.9, and 5.9+/-1.4 and 9.7+/-3.5 microM, respectively. The known compounds, daidzein (4) and 2'-Hydroxydaidzein (6), isolated from C. pallida, inhibited of the release of lysozyme and beta-glucuronidase from rat neutrophils in response to fMLP/CB with IC(50) values of 26.3+/-5.5 and 13.7+/-2.6 microM, respectively. Compounds 1 and 4 also showed significant concentration-dependent inhibitory effects on superoxide anion generation in rat neutrophils stimulated with fMLP/CB with IC(50) values of 3.4+/-0.3 and 25.1+/-5.0 microM, respectively. Compounds 1 and 5, previously isolated from C. pallida, showed the inhibition of NO production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages and LPS/interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma)-stimulated N9 microglial cells with IC(50) values of 10.7+/-0.1 and 13.9+/-1.1 microM, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
Flavonoids, suppressed chemical mediators in inflammatory cells, may have value in treatment and prevention of central and peripheral inflammatory diseases associated with excess production of chemical mediators. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)