| In vitro: |
| Phytochemistry. 2008 Jan;69(2):451-6. | | Antioxidant aryl-prenylcoumarin, flavan-3-ols and flavonoids from Eysenhardtia subcoriacea.[Pubmed: 17892888] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Antioxidant activity (AOA) assay-guided chemical analysis, using a rat pancreas homogenate model, of aerial parts from Eysenhardtia subcoriacea, led to isolation of the new compound subcoriacin (3-(2'-hydroxy-4',5'-methylendioxyphenyl)-6-(3''-hydroxymethyl-4''-hydroxybut-2''-enyl)-7-hydroxycoumarin) together with the known substances: (+)-catechin, (-)-epicatechin, (+)-Afzelechin, eriodictyol, (+)-catechin 3-O-beta-D-galactopyranoside and quercetin 3-O-beta-D-galactopyranoside as bioactive constituents. The structure of the compound was determined from 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopic analyses. Additional known constituents were characterized.
CONCLUSIONS:
The bioactive compounds showed also moderate to strong radical scavenging properties against diphenylpicrylhydrazyl radical (DPPH). In addition, subcoriacin, (+)-catechin, (-)-epicatechin and (+)-Afzelechin improved the reduced glutathione levels in rat pancreatic homogenate. | | Arch Pharm Res. 2005 Jul;28(7):804-9. | | Neuroprotective and free radical scavenging activities of phenolic compounds from Hovenia dulcis.[Pubmed: 16114495] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The EtOAc-soluble fraction from a methanolic extract of Hovenia dulcis Thunb. exhibited neuroprotective activity against glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in mouse hippocampal HT22 cells.
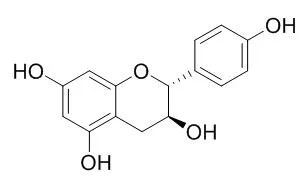
The neuroprotective activity-guided isolation resulted in 8 phenolic compounds (1-8), such as vanillic acid (1), ferulic acid (2), 3,5-dihydroxystilbene (3), (+)-aromadendrin (4), methyl vanillate (5), (-)-catechin (6), 2,3,4-trihydrobenzoic acid (7), and (+)-Afzelechin (8). Among these, compounds 6 and 8 had a neuroprotective effect on the glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in HT22 cells. Furthermore, compound 6 had a DPPH free radical scavenging effect with an IC50 value of 57.7 microM, and a superoxide anion radical scavenging effect with an IC50 value of 8.0 microM. Both compounds 6 and 8 had ABTS cation radical scavenging effects with IC50 values of 7.8 microM and 23.7 microM, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that compounds 6 and 8 could be neuroprotectants owing to their free radical scavenging activities. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)