| In vitro: |
| The Korean Journal of Pesticide Science,2006, 10(3):230-6. | | Antibacterial Activities against Plant Pathogens and Identification of Agrimol B from Agrimonia pilosa LEDEB.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Eighty-five percent methanol extract of Agrimonia pilosa has antibacterial activity against Pseudomonas syringae pv. lacrymans (bacterial leaf spot pathogen), Ralstonia solanacearum (tomato bacterial wilt pathogen) and Pseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci (Tobacco wild fire pathogen.). The active substance was purified by silica gel column chromatography and HPLC. The molecular weight of the active compound was determined by LC-Mass as 687.2.
CONCLUSIONS:
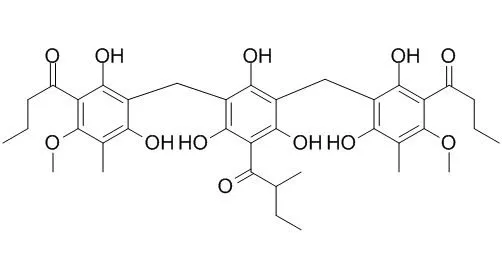
With NMR analysis, the active substance was identified as Agrimol B. | | Biochem Biophys Res Commun . 2016 Aug 26;477(3):454-60. | | Agrimol B suppresses adipogenesis through modulation of SIRT1-PPAR gamma signal pathway[Pubmed: 27320865] | | Abstract
Studies of human genetics have implicated the role of SIRT1 in regulating obesity, insulin resistance, and longevity. These researches motivated the identification of novel SIRT1 activators. The current study aimed to investigate the potential efficacy of Agrimol B, a polyphenol derived from Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb., on mediating SIRT1 activity and fat metabolism. Results showed that Agrimol B significantly induced cytoplasm-to-nucleus shuttle of SIRT1. Furthermore, we confirmed that Agrimol B dramatically inhibited 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation by reducing PPARγ, C/EBPα, FAS, UCP-1, and apoE expression. Consequently, adipogenesis was blocked by treatment of Agrimol B at the early stage of differentiation in a dose-dependent manner, the IC50 value was determined as 3.35 ± 0.32 μM. Taken together, our data suggest a therapeutic potential of Agrimol B on alleviating obesity, through modulation of SIRT1-PPARγ signal pathway.
Keywords: Agrimol B; Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb.; Lipid droplet; Obesity; PPARγ; SIRT1. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)