| Kinase Assay: |
| World Journal of Gastroenterology, 2009, 15(23):2870-7. | | Alisol B acetate induces apoptosis of SGC7901 cells via mitochondrial and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases/Akt signaling pathways.[Reference: WebLink] | To examine the effect of Alisol B acetate on the growth of human gastric cancer cell line SGC7901 and its possible mechanism of action.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The cytotoxic effect of Alisol B acetate on SGC7901 cells was measured by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. Phase-contrast and electron microscopy were used to observe the morphological changes. Cell cycle and mitochondrial transmembrane potential (Δψm) were determined by flow cytometry. Western blotting was used to detect the expression of apoptosis-regulated gene Bcl-2, Bax, Apaf-1, caspase-3, caspase-9, Akt, P-Akt and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases (PI3K).
Alisol B acetate inhibited the proliferation of SGC7901 cell line in a time- and dose-dependent manner. PI staining showed that Alisol B acetate can change the cell cycle distribution of SGC7901, increase the proportion of cells in G0-G1 phase and decrease the proportion of S phase cells and G2-M phase cells. Alisol B acetate at a concentration of 30 μmol/L induced apoptosis after 24, 48 and 72 h incubation, with occurrence rates of apoptotic cells of 4.36%, 14.42% and 21.16%, respectively. Phase-contrast and electron microscopy revealed that the nuclear fragmentation and chromosomal condensed, cells shrank and attachment loss appeared in the SGC7901 treated with Alisol B acetate. Apoptosis of SGC7901 cells was associated with cell cycle arrest, caspase-3 and caspase-9 activation, loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and up-regulation of the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2 and inhibition of the PI3K/Akt.
CONCLUSIONS:
Alisol B acetate exhibits an anti-proliferative effect in SGC7901 cells by inducing apoptosis. Apoptosis of SGC7901 cells involves mitochondria-caspase and PI3K/Akt dependent pathways. |
|
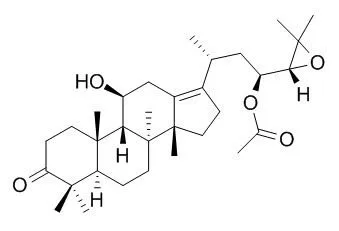
| Structure Identification: |
| J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol. 2013 Jan;36(4):513-524. | | Optimization of Extraction Condition for Alisol B and Alisol B Acetate in Alismatis Rhizoma using Response Surface Methodology.[Pubmed: 23335845] | Alismatis Rhizoma is a perennial herb originating from the rhizomes of Alisma orientalis (Sam) Juzep and the same species which have been used to treat seborrheic dermatitis, eczema, polydipsia, and pedal edema.
We aimed to determine the concentrations of the compounds alisol B and Alisol B acetate present in a sample of the herb using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with a photodiode array detector.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We selected methanol as the optimal solvent considering the structures of alisol B and Alisol B acetate. We estimated the proportion of alisol B and Alisol B acetate in a standard extract to be 0.0434% and 0.2365% in methanol, respectively. To optimize extraction, we employed response surface methodology to determine the yields of alisol B and Alisol B acetate, which mapped out a central composite design consisting of 15 experimental points.
The extraction parameters were time, concentration, and sample weight.
CONCLUSIONS:
The predicted concentration of alisol B derivatives was estimated to be 0.2388% under the following conditions: 81 min of extraction time, 76% of methanol concentration, and 1.52g of sample weight. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)