| In vitro: |
| Mol Cell Biol . 1997 Jun;17(6):3373-81. | | Ribotoxic stress response: activation of the stress-activated protein kinase JNK1 by inhibitors of the peptidyl transferase reaction and by sequence-specific RNA damage to the alpha-sarcin/ricin loop in the 28S rRNA[Pubmed: 9154836] | | Inhibition of protein synthesis per se does not potentiate the stress-activated protein kinases (SAPKs; also known as cJun NH2-terminal kinases [JNKs]). The protein synthesis inhibitor Anisomycin, however, is a potent activator of SAPKs/JNKs. The mechanism of this activation is unknown. We provide evidence that in order to activate SAPK/JNK1, Anisomycin requires ribosomes that are translationally active at the time of contact with the drug, suggesting a ribosomal origin of the Anisomycin-induced signaling to SAPK/JNK1. In support of this notion, we have found that aminohexose pyrimidine nucleoside antibiotics, which bind to the same region in the 28S rRNA that is the target site for Anisomycin, are also potent activators of SAPK/JNK1. Binding of an antibiotic to the 28S rRNA interferes with the functioning of the molecule by altering the structural interactions of critical regions. We hypothesized, therefore, that such alterations in the 28S rRNA may act as recognition signals to activate SAPK/JNK1. To test this hypothesis, we made use of two ribotoxic enzymes, ricin A chain and alpha-sarcin, both of which catalyze sequence-specific RNA damage in the 28S rRNA. Consistent with our hypothesis, ricin A chain and alpha-sarcin were strong agonists of SAPK/JNK1 and of its activator SEK1/MKK4 and induced the expression of the immediate-early genes c-fos and c-jun. As in the case of Anisomycin, ribosomes that were active at the time of exposure to ricin A chain or alpha-sarcin were able to initiate signal transduction from the damaged 28S rRNA to SAPK/JNK1 while inactive ribosomes were not. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Toxicol Lett . 2012 Jan 5;208(1):1-11. | | In vivo toxicological evaluation of Anisomycin[Pubmed: 22004851] | | Anisomycin is a pyrrolidine antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces griseolus. Recent studies have shown that Anisomycin as a novel immunosuppressive agent is superior to Cyclosporine A (J. Immunother. 31, 858-870, 2008). In order to make toxicological evaluation of Anisomycin, acute and four-week continuously intravenous toxicity studies were performed in mice. IC(50) value tested on peripheral lymphocytes was 25.44 ng/ml. The calculated LD(50) for Anisomycin was 119.64 mg/kg. The mice were intravenously injected through mouse tail vein with a total dose of 5, 15, 30 and 60 mg/kg/mice of Anisomycin every other day for 4 weeks. Just in the high-dose mice, death of three mice happened and body weight of the mice was significantly decreased. Statistically significant changes in organ index included increases in ratios of the spleen, liver, lung and brain to the body weight, and decrease in ratio of the thymus to the body weight. Changes in clinical biochemistry parameters included increases in the aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) activities, and decreases in the glucose (GLU) activity. The distinct inflammation appeared in the lung, liver and kidney, and the number and size of megakaryocytes in the spleen were significantly increased. Anisomycin did not induce formation of the peripheral blood micronucleus, but increased the number of micronucleated polychromatic erythrocytes in bone marrow and sperm aberrations. However, the above aberrant changes occurred only in the mice treated with the high-dose Anisomycin. These results indicate that although Anisomycin has no significant side effects at effectively therapeutic doses, its over-dosage may lead to toxicity, particularly pulmo-, nephro- and hepato-toxicity. | | Cardiovasc Res . 2018 Apr 1;114(5):737-746. | | Transcriptional regulation of stress kinase JNK2 in pro-arrhythmic CaMKIIδ expression in the aged atrium[Pubmed: 29360953] | | Aims: c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) is a critical stress response kinase that activates in a wide range of physiological and pathological cellular processes. We recently discovered a pivotal role of JNK in the development of atrial arrhythmias in the aged heart, while cardiac CaMKIIδ, another pro-arrhythmic molecule, was also known to enhance atrial arrhythmogenicity. Here, we aimed to reveal a regulatory role of the stress kinase JNK2 isoform on CaMKIIδ expression.
Methods and results: Activated JNK2 leads to increased CaMKIIδ protein expression in aged human and mouse atria, evidenced from the reversal of CaMKIIδ up-regulation in JNK2 inhibitor treated wild-type aged mice. This JNK2 action in CaMKIIδ expression was further confirmed in HL-1 myocytes co-infected with AdMKK7D-JNK2, but not when co-infected with AdMKK7D-JNK1. JNK2-specific inhibition (either by a JNK2 inhibitor or overexpression of inactivated dominant-negative JNK2 (JNK2dn) completely attenuated JNK activator Anisomycin-induced CaMKIIδ up-regulation in HL-1 myocytes, whereas overexpression of JNK1dn did not. Moreover, up-regulated CaMKIIδ mRNA along with substantially increased phosphorylation of JNK downstream transcription factor c-jun [but not activating transcription factor2 (ATF2)] were exhibited in both aged atria (humans and mice) and transiently JNK activated HL-1 myocytes. Cross-linked chromatin-immunoprecipitation assays (XChIP) revealed that both c-jun and ATF2 were bound to the CaMKIIδ promoter, but significantly increased binding of c-jun only occurred in the presence of Anisomycin and JNK inhibition alleviated this Anisomycin-elevated c-jun binding. Mutated CaMKII consensus c-jun binding sites impaired its promoter activity. Enhanced transcriptional activity of CaMKIIδ by Anisomycin was also completely reversed to the baseline by either JNK2 siRNA or c-jun siRNA knockdown.
Conclusion: JNK2 activation up-regulates CaMKIIδ expression in the aged atrium. This JNK2 regulation in CaMKIIδ expression occurs at the transcription level through the JNK downstream transcription factor c-jun. The discovery of this novel molecular mechanism of JNK2-regulated CaMKII expression sheds new light on possible anti-arrhythmia drug development. |
|


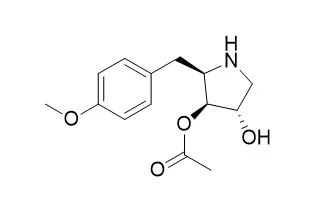



 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)