| Description: |
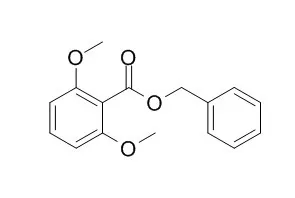
Benzyl 2,6-dimethoxybenzoate shows significant analgesic effects, it induces a concentration-dependent inhibition of the spontaneous contractions of the guinea-pig ileum with IC50 values ranging from 1.49 to 4.96 microM. Benzyl 2,6-dimethoxybenzoate shows antimicrobial activity against several bacteria (S. aureus, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and B. subtilis) and fungi (C. albicans and T. mentagrophytes).
|
| In vivo: |
| J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Aug 13;118(3):448-54. | | Antinociceptive, hypoglycemic and spasmolytic effects of Brickellia veronicifolia.[Pubmed: 18583074] | Brickellia veronicifolia (Kunth) Gray (Asteraceae) (BV) is broadly commercialized for treating gastrointestinal diseases (stomach aches, biliary colics and dyspepsia), arthritis, diabetes and painful inflammatory complaints. In order to complete the preclinical pharmacological profile of BV, first the antinociceptive effect of an organic extract (BVE) and isolated metabolites on the hot plate and writhing tests was assessed.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Then, their potential hypoglycemic effects were analyzed in normoglycemic and diabetic rats; in addition, an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) was performed. Finally, the spasmolytic activity of BVE was assessed in vivo using the gastrointestinal motility test (GMT) in mice.
The results revealed that BVE (100-600 mg/kg), 6-methoxysalicylic acid (1), 2-methoxybenzoic acid (2), Benzyl 2,6-dimethoxybenzoate (3), and taraxasteryl acetate (4) showed significant analgesic effects. Compounds 2 and 3 were the most active (1-100mg/kg) in the hot plate and writhing tests, respectively. In the antidiabetic assays, BVE (100mg/kg) showed an important hypoglycemic action. Furthermore, at the same dose, it provoked a significant postprandial decrease of blood glucose level after 30 min of a glucose challenge. Finally, the GMT in mice revealed the spasmolytic activity in vivo of BVE (31.6 mg/kg).
CONCLUSIONS:
The overall information tends to support the vernacular uses of the plant. | | Planta Med. 2005 Apr;71(4):320-5. | | Smooth muscle relaxant action of benzyl benzoates and salicylic acid derivatives from Brickellia veronicaefolia on isolated guinea-pig ileum.[Pubmed: 15856407] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A dichloromethane-MeOH extract prepared from the aerial parts of Brickellia veronicaefolia inhibited the spontaneous contractions (IC50 = 39.22 microg/mL) of the guinea-pig ileum. Bioassay-guided fractionation of the extract led to the isolation of three new benzoic acid derivatives, 1,2-bis-O-(2-methoxybenzoyl)-beta-d-glucopyranoside (1), 3-(beta-glucopyranosyloxy)Benzyl 2,6-dimethoxybenzoate (2) and 3-hydroxyBenzyl 2,6-dimethoxybenzoate (3), together with the known compounds taraxasteryl acetate (4), 4-allyl-2-methyloxyphenyl-beta-glucopyranoside (5), 2-hydroxy-6-methoxybenzoic acid (6), 2-methoxybenzoic acid (7), chamazulene (8), 2-methoxybenzyl 2-hydroxybenzoate (9), Benzyl 2,6-dimethoxybenzoate (10), 3-methoxybenzyl 2-hydroxy-6-methoxybenzoate (11), benzyl 2-hydroxy-6-methoxybenzoate (12), benzyl 2,3,6-trimethoxybenzoate (13), benzyl 2-hydroxy-3,6-dimethoxybenzoate (14) and 3-methoxyBenzyl 2,6-dimethoxybenzoate (15). The isolates were characterized by spectral means.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 2 - 6, 8 - 11, 14 and 15 induced a concentration-dependent inhibition of the spontaneous contractions of the guinea-pig ileum with IC50 values ranging from 1.49 to 4.96 microM. Their activity was comparable to that of papaverine (IC50 = 4.23 microM). |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)