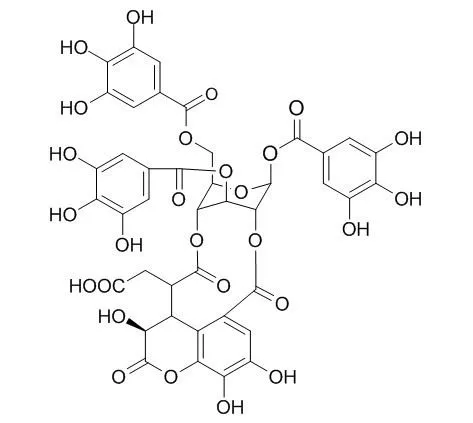
| Description: |
Chebulinic acid is a potent natural inhibitor of M. tuberculosis DNA gyrase, also can inhibit SMAD-3 phosphorylation, inhibit H+ K+-ATPase activity; it also is a natural inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor-A mediated angiogenesis. Chebulinic acid has hypotensive, antioxidant, anti-HIV, and anti-ulcer activities. Chebulinic acid has inhibitory effect on erythroid differentiation likely through changing transcriptional activation of differentiation relative genes, it or other tannins might influence the efficiency of some anti-tumor drugs-induced differentiation or the hematopoiesis processes.
|
| Targets: |
ATPase | Potassium Channel | VEGFR | HIV | Antifection | GATA-1 | PBGD | NF-E2 |
| In vitro: |
| Toxicol In Vitro. 2009 Jun;23(4):667-73. | | Chebulinic acid and tellimagrandin I inhibit DNA strand breaks by hydroquinone/Cu(II) and H(2)O(2)/Cu(II), but potentiate DNA strand breaks by H(2)O(2)/Fe(II).[Pubmed: 19328845] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The effects of two polyphenols, Chebulinic acid and tellimagrandin I, on DNA strand breaks mediated by H(2)O(2)/Cu(II), hydroquinone (HQ)/Cu(II) and H(2)O(2)/Fe(II) in pBR322 plasmid DNA and genomic DNA of cultured MRC-5 human embryo lung fibroblasts were examined. The results demonstrated that Chebulinic acid and tellimagrandin I obviously inhibited HQ/Cu(II)- and H(2)O(2)/Cu(II)-mediated pBR322 DNA strand breaks. When MRC-5 cells were treated with HQ/Cu(II), the presence of Chebulinic acid or tellimagrandin I inhibited HQ/Cu(II)-mediated double strand breaks of genomic DNA. The presence of Chebulinic acid or tellimagrandin I did not affect the H(2)O(2)- and HQ-mediated reduction of Cu(II) to Cu(I). Both polyphenols could slightly inhibit H(2)O(2)/Fe(II)-mediated plasmid DNA strand break at the lower concentration (1-10 microM), but potentiate the DNA strand break at the higher concentration (over 50 microM).
CONCLUSIONS:
These results demonstrated that Chebulinic acid and tellimagrandin I possessed antioxidant action in certain conditions and exerted prooxidant action on DNA strand breaks in other conditions. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1996 Aug;23(8):747-50. | | In vitro inhibitory effects of chebulinic acid on the contractile responses of cardiovascular muscles.[Pubmed: 8886502] | 1. The effects of Chebulinic acid, which has been shown to elicit blood pressure lowering effect in rats, on aortic vascular contraction as well as cardiac contraction were studied in rats.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
2. Chebulinic acid had no effect on KCl-induced aortic contraction, but irreversibly inhibited the contractile responses to phenylephrine in an apparently non-competitive manner. Chebulinic acid also inhibited contractile responses of rat aorta to 5-hydroxytryptamine and angiotensin II. 3. Chebulinic acid inhibited the binding of [3H]-prazosin to dog aortic microsomal membranes in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC50 value of 0.34 mmol/L. Results of saturation binding experiments suggest a mixed mode of inhibition by Chebulinic acid (i.e. a decrease in both the maximal number of binding sites and the affinity for prazosin). 4. Chebulinic acid concentration-dependently and reversibly inhibited the maximal left ventricular pressure of rat heart in a Langendorff preparation with 50% inhibition occurring at a concentration of 0.3 nmol/L. 5. We conclude that Chebulinic acid exerts non-specific inhibitory actions in vascular preparations. Its inhibitory effect on cardiac contraction was reversible and three orders of magnitude more potent than that on vascular contraction.
CONCLUSIONS:
We suggest that the hypotensive effect of Chebulinic acid is probably mediated via the decrease in cardiac output resulting from reduced left ventricular contraction. | | Phytomedicine. 2013 Apr 15;20(6):506-11. | | Anti-secretory and cyto-protective effects of chebulinic acid isolated from the fruits of Terminalia chebula on gastric ulcers.[Pubmed: 23462212] | In continuation of our drug discovery program on Indian medicinal plants, the gastro protective mechanism of Chebulinic acid isolated from Terminalia chebula fruit was investigated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Chebulinic acid was evaluated against cold restraint (CRU), aspirin (AS), alcohol (AL) and pyloric ligation (PL) induced gastric ulcer models in rats. Potential anti-ulcer activity of Chebulinic acid was observed against CRU (62.9%), AS (55.3%), AL (80.67%) and PL (66.63%) induced ulcer models. The reference drug omeprazole (10 mg/kg, p.o.) showed 77.73% protection against CRU, 58.30% against AS and 70.80% against PL model. Sucralfate, another reference drug (500 mg/kg, p.o.) showed 65.67% protection in AL induced ulcer model. Chebulinic acid significantly reduced free acidity (48.82%), total acidity (38.29%) and upregulated mucin secretion by 59.75% respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
Further, Chebulinic acid significantly inhibited H(+) K(+)-ATPase activity in vitro with IC50 of 65.01 μg/ml as compared to the IC50 value of omeprazole (30.24 μg/ml) confirming its anti-secretory activity. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)