| Description: |
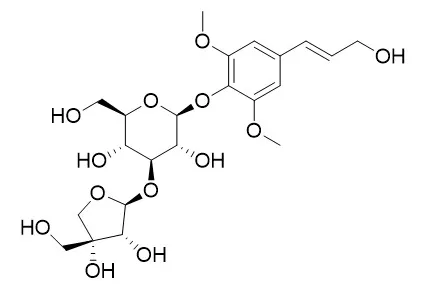
Cordifolioside A possesses immunomodulatory activity, it has a potential in vivo radioprotective effect as well as in vitro cytoprotective activity. |
| Targets: |
Immunology & Inflammation related |
| In vitro: |
| J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Jun 14;141(3):918-26. | | Immunomodulatory active compounds from Tinospora cordifolia.[Pubmed: 22472109] | Tinospora cordifolia mentioned as "Rasayana" is extensively used in various herbal preparations for the treatment of different ailments for its general tonic, antiperiodic, antispasmodic, antiinflammatory, antiarthritic, antiallergic and antidiabetic properties. It is extensively used in Ayurveda due to its potential in improving the immune system and the body resistance against infections. The aim of the study was to isolate and characterise the immunomodulatory active compounds of Tinospora cordifolia.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The immunomodulatory activity of different extracts, fractions and isolated compounds in relation to phagocytosis and reactive oxygen species production in human neutrophil cells have been investigated using the PMN phagocytic function studies, NBT, NO and chemiluminescence assay. The results obtained indicate that ethyl acetate, water fractions and hot water extract exhibited significant immunomodulatory activity with an increase in percentage phagocyctosis. Chromatographic purification of these fraction led to the isolation of a mixture of two compounds 2, 3 isolated for the first time from natural source and five known compounds 1, 4-7 which were characterized as 11-hydroxymustakone (2), N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (3), N-formylannonain (1), Cordifolioside A (4), magnoflorine (5), tinocordiside (6), syringin (7) by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mass spectrometry (MS) and comparing the spectral data with reported one. Cordifolioside A and syringin have been reported to possess immunomodulatory activity. Other five compounds showed significant enhancement in phagocytic activity and increase in nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species generation at concentration 0.1-2.5 μg/ml.
CONCLUSIONS:
Seven immunomodulatory active compounds belonging to different classes have been isolated and characterised indicating that the immunomodulatory activity of Tinospora cordifolia may be attributed to the synergistic effect of group of compounds. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Indian J Pharmacol. 2013 May-Jun;45(3):237-43. | | Radioprotective and cytoprotective activity of Tinospora cordifolia stem enriched extract containing cordifolioside-A.[Pubmed: 23833365] | The present study was undertaken to evaluate the radioprotective and cytoprotective potential of Cordifolioside A, a primary active constituent of n-butanol fraction of Tinospora Cordifolia (NBTC) against 4 Gy-γ radiation in mice and cyclophosphamide induced genotoxicity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Presence of Cordifolioside A in NBTC stem ethanolic extract was confirmed by high performance thin layer chromatography (HPTLC) analysis. Radioprotective activity was evaluated at 80 and 120 mg/kg, intraperitoneal (i.p.) dose of NBTC administered 15 days prior to whole body radiation exposure by observing survival rate, change in body weight, hematology, spleen colony forming unit (CFU), and micronucleus (MN) expression. Cytoprotective activity of NBTC was evaluated at 5, 10, and 15 mg/ml concentrations on Allium cepa root meristem growth against cyclophosphamide. HPTLC analysis of standard Cordifolioside A, and NBTC confirmed the presence of cordifolioside-A in NBTC with the retention factor value of 0.86. Administration of NBTC (120 mg/kg, i.p.) produced significant protection against radiation in terms of increased survival rate, body weight retention, hematological parameters, spleen CFU assay (P < 0.01), and decreased MN expression (P < 0.01). Cytoprotectivity was observed maximally at 10 mg/ml NBTC concentration with significant increase in root growth (P < 0.01), non-toxic mitotic index (MI) (65.9%) and lesser chromosomal aberrations (15.4%). NBTC at 10 mg/ml concentration showed very few C-anaphase compared to aberrations like fragmentation, C-anaphase, multipolarity and sticky chromosome in cyclophosphamide alone.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results suggest that enriched NBTC containing Cordifolioside A has a potential in vivo radioprotective effect as well as in vitro cytoprotective activity. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)