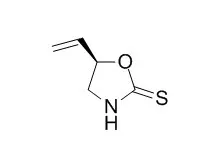
| Structure Identification: |
| J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Nov 18;157:55-61. | | In vitro antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of Radix Isatidis extract and bioaccessibility of six bioactive compounds after simulated gastro-intestinal digestion.[Pubmed: 25256688] | Radix Isatidis called "Ban-Lan-Gen" is one of the most commonly-used traditional Chinese medicines for antiviral, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and antipyretic purposes. Investigate the bioaccessibility of uridine, Epigoitrin, adenosine, clemastanin B, indigoticoside A and isolariciresinol as well as the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities during an in vitro gastro-intestinal digestion of the Radix Isatidis extract (RIE).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) technique was adopted to determine the bioaccessibility of six bioactive compounds in RIE. Antioxidant activities of RIE in different digestive stages were determined by 1,1-Diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), superoxide anion and hydroxyl radical scavenging abilities. Anti-inflammatory activity was assayed by the inhibitions of inflammatory cytokines such as nitrous oxide (NO), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and tumor necrosis factor α(TNF-α) producted by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulated RAW264.7 cells.
The bioaccessibility of uridine, Epigoitrin, adenosine, clemastanin B, indigoticoside A and isolariciresinol were 15.38%, 18.28%, 24.01%, 6.50%, 8.65% and 17.78%, respectively. Also, the digestion products still possessed certain antioxidant activities. The antioxidant activity was highly correlated with lignans (clemastanin B, indigoticoside A and isolariciresino). The anti-inflammation activity of the three samples decreased in the order: IN sample (the solution that had diffused into the dialysis tubing)>Nondigested sample (RIE solution)>Gastric sample (post-gastric digestion)>OUT sample (material that remained in the gastro-intestinal tract).
CONCLUSIONS:
Results obtained in this research reveal the amount of bioactive compounds from RIE that could be available for absorption in vivo. The antioxidant activity decreased significantly but the anti-inflammatory activity was enhanced in serum-available fraction after gastro-intestinal digestion in vitro. This study could provide a scientific basis for a deeper pharmacological activity study of Radix Isatidis and a simple method for pharmacodynamic material basis research. | | Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2008 Sep;33(18):2074-6. | | [Content determination of epigoitrin in Radix Isatidis and its preparation by RP-HPLC].[Pubmed: 19160787] | To establish an HPLC method for the content determination of Epigoitrin in Radix Isatidis and its preparation, and to provide valuable data for quality control of Radix Isatidis and its preparation.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The samples were separated on a ZORBAX SB-C18 (4. 6 mm x 150 mm, 5 microm) column with the mobile phase of acetonitrile-water-phosphoric acid-triethylamine (8.50 : 90.72 : 0.73 : 0.05) in the flow rate of 0.7 mL x min(-1). The detection wavelength was set at 245 nm. Column temperature was 30 degrees C.
The linear range of Epigoitrin was 0.0204-0.3060 microg (r = 0.9998), and the average recovery was 98.99% with the RSD was 1.31% (n = 9).
CONCLUSIONS:
The method for quantitation of Epigoitrin in Radix Isatidis and its preparation was accurate and reliable, which can be used to evaluate the quality of Radix Isatidis and its preparation.
|
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)