| In vitro: |
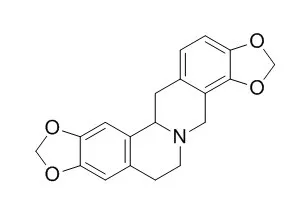
| FEBS J. 2007 Feb;274(4):1019-35. | | Molecular cloning and characterization of methylenedioxy bridge-forming enzymes involved in stylopine biosynthesis in Eschscholzia californica.[Pubmed: 17250743] | (S)-Stylopine is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of benzophenanthridine alkaloids, such as sanguinarine. Stylopine biosynthesis involves the sequential formation of two methylenedioxy bridges.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Two cytochrome P450 cDNAs involved in Stylopine biosynthesis were isolated using degenerate primers designed for C. japonica CYP719 from cultured Eschscholzia californica cells. Heterologous expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae showed that both CYP719A2 and CYP719A3 had Stylopine synthase activity to catalyze methylenedioxy bridge-formation from cheilanthifoline to Stylopine, but not cheilanthifoline synthase activity to convert scoulerine to cheilanthifoline. Functional differences and expression patterns of CYP719A2 and CYP719A3 were examined to investigate their physiological roles in Stylopine biosynthesis. Enzymatic analysis showed that CYP719A2 had high substrate affinity only toward (R,S)-cheilanthifoline, whereas CYP719A3 had high affinity toward three similar substrates (R,S)-cheilanthifoline, (S)-scoulerine, and (S)-tetrahydrocolumbamine.
CONCLUSIONS:
An expression analysis in E. californica plant tissues showed that CYP719A2 and CYP719A3 exhibited expression patterns similar to those of three Stylopine biosynthetic genes (CYP80B1, berberine bridge enzyme, and S-adenosyl-l-methionine : 3'-hydroxy-N-methylcoclaurine 4'-O-methyltransferase), whereas the specific expression of CYP719A3 in root was notable. Treatment of E. californica seedlings with methyl jasmonate resulted in the coordinated induction of CYP719A2 and CYP719A3 genes. The physiological roles of CYP719A2 and CYP719A3 in Stylopine biosynthesis are discussed. | | Arch Pharm Res. 2004 Sep;27(9):923-9. | | Stylopine from Chelidonium majus inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory mediators in RAW 264.7 cells.[Pubmed: 15473662] | Stylopine is a major component of the leaf of Chelidonium majus L. (Papaveraceae), which has been used for the removal of warts, papillomas and condylomas, as well as the treatment of liver disease, in oriental countries.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Stylopine per se had no cytotoxic effect in unstimulated RAW 264.7 cells, but concentration-dependently reduced nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta), and the IL-6 production and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) activity caused by the LPS stimulation. The levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and COX-2 protein expressions were markedly suppressed by Stylopine in a concentration dependent manner.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that Stylopine suppress the NO and PGE2 production in macrophages by inhibiting the iNOS and COX-2 expressions. These biological activities of Stylopine may contribute to the anti-inflammatory activity of Chelidonium majus. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)