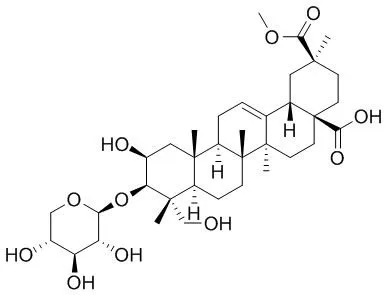
| Structure Identification: |
| J. Nat. Prod., 2008, 71(10):1720-5. | | Evidence for the mechanism of action of the antifungal phytolaccoside B isolated from Phytolacca tetramera Hauman.[Pubmed: 18816139 ] | Phytolaccoside B (Esculentoside B,1), an antifungal monodesmoside triterpenoid glycoside isolated from berries of Phytolacca tetramera Hauman (Phytolaccaceae), alters the morphology of yeasts and molds.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The malformations were similar to those produced by enfumafungin, a known inhibitor of (1-->3)-beta-D-glucan synthase, an enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of (1-->3)-beta-D-glucan, one of the major polymers of the fungal cell wall. However, enzymatic assays revealed that 1 did not inhibit (1-->3)-beta-D-glucan synthase, but it did produce a notable enhancement of the chitin synthase 1 activity and, concomitantly, a rise in chitin, another important polymer of the fungal cell walls.
CONCLUSIONS:
This finding was corroborated by fluorescence microscopy and also by quantification of the chitin. In addition, a 2-fold increase in the thickness of the fungal cell wall was observed with transmission electronic microscopy. On the other hand, 1 neither bound to ergosterol nor caused hemolysis of red blood cells, although some fungal membrane damage was observed at the MIC of 1. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)