| Structure Identification: |
| Org Lett. 2015 Feb 6;17(3):628-31. | | Discovery of a new family of Dieckmann cyclases essential to tetramic acid and pyridone-based natural products biosynthesis.[Pubmed: 25621700] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Bioinformatic analyses indicate that TrdC, SlgL, LipX2, KirHI, and FacHI belong to a group of highly homologous proteins involved in biosynthesis of actinomycete-derived tirandamycin B, streptolydigin, α-lipomycin, kirromycin, and factumycin, respectively. However, assignment of their biosynthetic roles has remained elusive.
CONCLUSIONS:
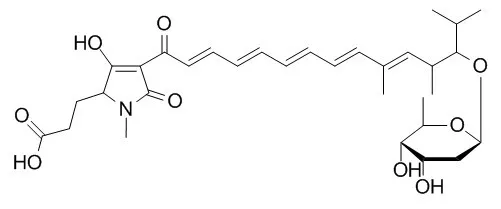
Gene inactivation and complementation, in vitro biochemical assays with synthetic analogues, point mutations, and phylogenetic tree analyses reveal that these proteins represent a new family of Dieckmann cyclases that drive tetramic acid and pyridone scaffold biosynthesis. | | Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2014 Jul 7;53(28):7328-34. | | α- and β-Lipomycin: total syntheses by sequential stille couplings and assignment of the absolute configuration of all stereogenic centers.[Pubmed: 24895187] | 40 years ago spectroscopy, derivatization, and degradation revealed the structures of alpha-Lipomycin and its aglycon β-lipomycin except for the configurations of their side-chain stereocenters.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We synthesized all relevant β-lipomycin candidates: the (12R,13S) isomer has the same specific rotational value as the natural product. By the same criterion the (12R,13S)-configured D-digitoxide is identical to alpha-Lipomycin.
CONCLUSIONS:
We double-checked our assignments by degrading alpha-Lipomycin and β-lipomycin to the diesters 33 and 34 and proving their 3D structures synthetically. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)