| J Agric Food Chem. 2008 Jun 11;56(11):3973-80. |
| Lucidenic acid B induces apoptosis in human leukemia cells via a mitochondria-mediated pathway.[Pubmed: 18481862] |
Ganoderma lucidum is known as a medicinal mushroom used in traditional Chinese medicine.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, the effect of lucidenic acids (A, B, C, and N) isolated from a new G. lucidum (YK-02) on induction of cell apoptosis and the apoptotic pathway in HL-60 cells were investigated. The results demonstrated that lucidenic acids decreased cell population growth of HL-60 cells, assessed with the MTT assay. The cell cycle assay indicated that treatment of HL-60 cells with lucidenic acid A, C, and N caused cell cycle arrest in the G 1 phase. Lucidenic acid B (LAB) did not affect the cell cycle profile; however, it increased the number of early and late apoptotic cells but not necrotic cells. Treatment of HL-60 cells with LAB caused loss of mitochondria membrane potential. Moreover, the ratio of expression levels of pro- and antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family members was changed by LAB treatment. LAB-induced apoptosis involved release of mitochondria cytochrome c and subsequently induced the activation of caspase-9 and caspase-3, which were followed by cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP).
CONCLUSIONS:
Pretreatment with a general caspase-9 inhibitor (Z-LEHD-FMK) and caspase-3 inhibitor (Z-DEVD-FMK) prevented LAB from inhibiting cell viability in HL-60 cells.
Our finding may be critical to the chemopreventive potential of Lucidenic acid B. |
| Mol Nutr Food Res. 2007 Dec;51(12):1472-7. |
| The anti-invasive effect of lucidenic acids isolated from a new Ganoderma lucidum strain.[Pubmed: 17979098] |
Ganoderma lucidum is a well-known mushroom with various pharmacological effects that has been used for health and longevity purposes.
The objective of this study was to investigate the anti-invasive effect of lucidenic acids isolated from a new G. lucidum strain (YK-02) against human hepatoma carcinoma (HepG(2)) cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Triterpenoid components in the ethanol extract of G. lucidum (YK-02) were separated by means of a semi-preparative RP HPLC. Four major peaks were separated and crystallized from triterpenoids fraction, and were identified as lucidenic acid A, Lucidenic acid B, lucidenic acid C, and lucidenic acid N according to their spectroscopic values of (1)H NMR and MS. Treatment of the lucidenic acids (50 microM) in the presence of 200 nM phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) after 24 h of incubation all resulted in significant inhibitory effects on PMA-induced MMP-9 activity and invasion of HepG(2 )cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results indicate that the lucidenic acids isolated from G. lucidum (YK-02) are anti-invasive bioactive components on hepatoma cells. |
| Phytother Res. 1999 Sep;13(6):529-31. |
| Triterpene antioxidants from ganoderma lucidum.[Pubmed: 10479768] |
Ganoderma lucidum was studied for its antioxidative activity by bioassay guided isolation in conjunction with in vitro tests.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The powdered crude drug was treated with boiling water and the aqueous extract (Ex1) was further separated to obtain terpene and polysaccharide fractions. The two fractions and Ex1 were screened for their antioxidative effect against pyrogallol induced erythrocyte membrane oxidation and Fe (II)-ascorbic acid induced lipid peroxidation.
CONCLUSIONS:
All tested samples showed antioxidative activities in a dose dependent manner and the terpene fraction was found to possess the highest effect compared with the others.
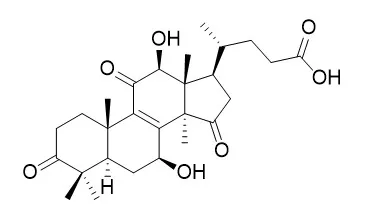
Chemical isolation of the terpene fraction resulted in the detection of ganoderic acid A, ganoderic acid B, ganoderic acid C and ganoderic acid D, Lucidenic acid B and ganodermanontriol as major ingredients. |





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)