| Kinase Assay: |
| J Ethnopharmacol. 2009 Jan 12;121(1):117-22. | | Effects of strictosamide on mouse brain and kidney Na+, K+-ATPase and Mg2+-ATPase activities.[Pubmed: 18992802] |
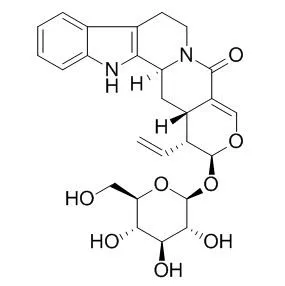
Present study reports on the general bioactivity of Strictosamide and on its effects on Na(+),K(+)-ATPase and Mg(2+)-ATPase activities of Charles River male mouse. Strictosamide is the main glycoalkaloid of Sarcocephalus latifolius (Rubiaceae) leaves and roots, used as medicinal plant in folk medicine.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this work, we studied the in vitro effects of various concentrations of Strictosamide (0.25, 0.5, 1 or 2 mg/mL) and the in vivo effects of single doses (50, 100 or 200 mg/kg, i.p.) of this compound on kidney and brain Na(+),K(+)-ATPase and Mg(2+)-ATPase activities. Results of general study showed that Strictosamide is slightly toxic to Charles River mouse (LD(50)=723.17 mg/kg), producing CNS depression and kidney toxicity, but the exact mechanism of these effects could not be defined.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Strictosamide inhibited the in vitro and in vivo Mg(2+)-ATPase activity on kidney but had nonsignificant effect on brain. Furthermore, Strictosamide had nonsignificant in vitro and in vivo effect on kidney Na(+),K(+)-ATPase activity but produced an in vivo increase of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase activity of brain, these findings suggesting that strictosamine may be related to the induction of alpha(2) isoform of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase and may account for the folk use of Sarcocephalus latifolius root infusion on hypertension. |
|
| Animal Research: |
| Pharm Biol. 2014 Nov;52(11):1445-50. | | In vivo anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of strictosamide from Nauclea officinalis.[Pubmed: 25026342] |
Strictosamide is the main representative constituent of Nauclea officinalis Pierre ex Pitard (Rubiaceae), which has been used for a long time in China to treat diseases related to infection and inflammation, but its pharmacological activities are not well studied.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
This work evaluates the anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of Strictosamide by in vivo experiments. At 20 and 40 mg/kg, Strictosamide obviously decreased the TPA-induced mice ear edema (24.7 and 28.1% inhibition, respectively), and significantly inhibited acetic acid-stimulated peritoneal vascular permeability in mice (23.3 and 33.4% inhibition, respectively). It also significantly decreased the leukocytes in the mice peritoneal cavity induced by CMC-Na at all the tested doses (46.0, 49.1, and 58.7% inhibition, respectively). To acetic acid-induced writhing test in mice, Strictosamide markedly prolonged the pain latency at 20 and 40 mg/kg and decreased the writhing counts at 40 mg/kg (49.7% inhibition). However, it did not obviously improve the pain threshold of mice in hot-plate test.
CONCLUSIONS:
Strictosamide may have important effects on inflammation and inflammatory pain. The results provide scientific support for the role of Strictosamide in the use of N. officinalis to treat inflammatory diseases. | | Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2012,18(15):170-4. | | Antibacterial and Antiviral Effects of Strictosamide.[Reference: WebLink] | To observe the antibacterial and antiviral activities,and provide certain experimental data for Strictosamide that is intended for upper respiratory tract infection.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The in vitro antibacterial activities on standard staphylococcus aureus and other 9 strains were observed by both test-tube and plating methods,and the protective effects on mice infected by staphylococcus aureus and streptococcus pneumonia were also observed.Mice were divided into 5 groups,such as normal group,model group,reduning group(crude drugs 8.7 g·kg-1),low and high dosage(20,40 mg·kg-1) of Strictosamide groups.They were injected intraperitoneally once a day for 7 days.At 1 h after the last injection,staphylococcus aureus or streptococcus pneumonia was injected intraperitoneally to mice,and then the death of mice was observed within 7 days.The in vitro antiviral activities were observed on the model of MDCK cells infected by influenza A(A/PR8/34(H1N1)) and B(B/Jingfang 98-76) virus,and the in vivo antiviral activities were observed by the model of mice infected by influenza A virus.Mice were divided into 5 groups,such as normal group,model group,reduning group(crude drugs 8.7 g·kg-1),low and high dosage(20,40 mg·kg-1) of Strictosamide groups.They were injected intraperitoneally once a day for 5 days,and virus was given to mice by nose on the first day.After the last injection,the lung lesions and pathological changes were observed,and the pulmonary index was also calculated. Strictosamide had inhibiting effects on standard escherichia coli and other 6 strains in vitro with MIC of 5 g·L-1.At 10 g·L-1,the diameters of inhibiting bacteria circle of diplococcus pneumonia and other 4 strains were 13-25 mm.At 40 mg·kg-1,the survival rate of mice infected by staphylococcus aureus and streptococcus pneumonia was 70% and 55%,separately.Strictosamide showed inhibitory effects on both influenza A and B viruses in vitro with IC50 values of 0.649,0.323 g·L-1,respectively.It also significantly inhibited increased pulmonary index and improved pulmonary pathological lesions of the infected mice caused by influenza A virus,and the inhibitory rate of pulmonary index was 39.8% at 40 mg·kg-1.
CONCLUSIONS:
Strictosamide possesses antibacterial and antiviral activities. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)