| In vitro: |
| Phytochemistry. 2002 May;60(2):163-6. | | Antifeedant activity of an anthraquinone aldehyde in Galium aparine L. against Spodoptera litura F.[Pubmed: 12009319] | The insect antifeedant anthraquinone aldehyde nordamnacanthal (1,3-dihydroxy-anthraquinone-2-al) was identified in Galium aparine L., and isolated from the root powder of akane (Rubia akane), a member of the Rubiaceae.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies using a series of anthraquinone analogues suggested that the aldehyde group on the anthraquinone was more important than the quinone moiety for antifeedant activity against the common cutworm (Spodoptera litura). High levels of nordamnacanthal were found in the seed leaf stage and in callus tissue induced from seedlings of G. aparine, but its concentration decreased with plant development. Since these compounds are natural pigments for dying textiles, we also evaluated the antifeedant activity against the carpet beetle (Attagenus japonicus ), a textile pest was also evaluated. While nordamnacanthal had strong antifeedant activity against the common cutworm, it did not show any antifeedant activity against the carpet beetle.
CONCLUSIONS:
The most effective antifeedant against the carpet beetle was the major constituent in the extract of R. trictorum, Lucidin 3-O-primeveroside, a food pigment. | | Biol Pharm Bull. 1998 Jun;21(6):641-2. | | Anthraquinones from Neonauclea calycina and their inhibitory activity against DNA topoisomerase II.[Pubmed: 9657055] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In a series of searches for DNA topoisomerase II inhibitors from naturally occurring compounds, a wood extract of Neonauclea calycina MERR. (Rubiaceae) showed a moderate effect in vitro.
Purification of the extract resulted in the isolation of seven known anthraquinones. The structures were characterized as damnacanthal, rubiadin 1-methyl ether, nordamnacanthal, morindone, damnacanthol, Lucidin 3-O-primeveroside and morindone 6-O-primeveroside by spectral analysis, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
Damnacanthal and morindone showed an intensive inhibitory effect against topoisomerase II (IC50: 20 micrograms/ml and 21 micrograms/ml). | | Walailak Journal of Science & Technology, 2012, 9(3). | | Distribution of Naturally Occurring Anthraquinones, Iridoids and Flavonoids from Morinda genus: Chemistry and Biological activity.[Reference: WebLink] | The present review covers chemistry and bioactivities of anthraquinones, iridoids, and flavonoids from the Morindagenus.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The plants of Morindaspecies, belonging to the Rubiaceae family, have been used as traditional folk medicine with anti-bacterial,anti-fungal, anti-tumor, anti-helmin, analgesic, antiinflammatory, and immune enhancing effects. They are rich sources of anthraquinones and iridoids. The relevant 2-methoxy-1,3,6-trihydroxyanthraquinone is one of the most potent quinone reductase enzyme inducers with no cytotoxicity with normal cells.
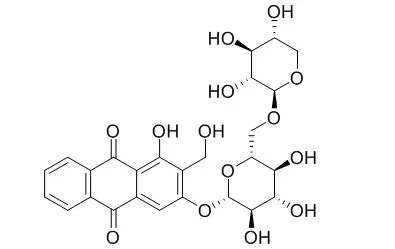
Damnacanthol-3-O-β-D-primeveroside and lucidin-3-O-β-D-primeveroside(Lucidin 3-O-primeveroside ) displayed a significant reduction of the blood glucose levels in anti-diabetic tests. Additionally, iridoids, 9-epi-6α-methoxy geniposidic acid,scandoside methyl ester, asperulosidic acid, showed a more potent inhibitory effect of melanogenesis than the commercial available depigmented arbutin used in cosmetic industry. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)