| In vitro: |
| Chemotherapy. 2014;60(2):81-7. | | In vitro Anticancer Activity of Myricanone in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells.[Pubmed: 25720464] | Myricanone, a typical large ring of cyclic diarylheptanoids, is abundant in the bark of Myrica. Our studies have found that Myricanone exerts potent anticancer activity. This study aimed to investigate the underlying mechanism of the effect of Myricanone on A549 cells in vitro.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A549 cells were treated with different concentrations of Myricanone for the following assays. Tritiated thymidine incorporation was used to measure growth inhibition. Flow cytometry was used to detect apoptosis and cell cycle progression, and colony formation was performed to observe the effect of Myricanone on the A549 proliferation rate. Myricanone induced significant dose-dependent growth inhibitory effects on A549 cells with an IC50 of 3.22 µg/ml. A significant decrease in colony formation was observed. This decrease induced cell apoptosis, G1 phase arrest and the emergence of the sub-G0 peak in A549 cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that Myricanone exhibits anticancer activity and may be applicable in the clinical prevention and treatment of lung cancer in the future. | | J Acupunct Meridian Stud. 2013 Aug;6(4):188-98. | | Anticancer potential of myricanone, a major bioactive component of Myrica cerifera: novel signaling cascade for accomplishing apoptosis.[Pubmed: 23972241] | Extract of Myrica cerifera bark has long been fruitfully used as a hepato-protective and anti-cancer drug in various complementary and alternative systems of medicine. Myricanone, its principal bioactive compound, had also been reported to have apoptosis-promoting ability.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We evaluated its anti-cancer potential in vitro in HepG2 liver cancer cells and tried to understand the signal cascades involved in accomplishing apoptosis. Further, we ascertained by using a (3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay (MTT) assay if it had cytotoxic effects on normal noncancerous liver cells (WRL-68). We deployed various tools and protocols, like phase contrast, scanning electron and fluorescence microscopies, performed an annexinV-FITC/PI assay and cell cycle analysis, and estimated the reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and mitochondrial membrane depolarization through flow cytometry. Further, analyses of cytochrome-c translocation and of HSP70 and caspase expressions were also done by using immunoblota and Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Results revealed that Myricanone induced apoptosis in HepG2 cells through generation of ROS, depolarization of the mitochondrial membrane, early release of cytochrome-c, down-regulation of HSP70 and activation of a caspase cascade; it had no, or insignificant, cytotoxic effects in WRL-68 cells in vitro and in mice in vivo.
CONCLUSIONS:
Thus, Myricanone has great potential for use in formulating an effective drug against both hepatotoxicity and hepatocellular cancer. | | Biol Pharm Bull. 2001 Mar;24(3):259-63. | | Anti-androgenic activity of Myricae Cortex--isolation of active constituents from bark of Myrica rubra.[Pubmed: 11256481] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The aqueous ethanol extract of Myricae Cortex (bark of Myrica rubra Sieb. et Zucc., Myricaceae) showed in vitro testosterone 5alpha-reductase inhibitory activity and in vivo anti-androgenic activity using growth of flank organ in castrated Syrian hamsters and/or hair regrowth after shaving in testosterone-treated C57Black/6CrSlc mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
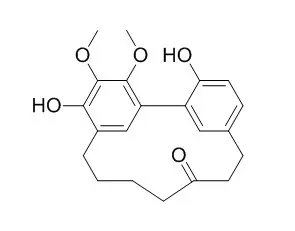
Three constituents, Myricanone, myricanol, and myricetin were identified as the main active principles. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)