| In vitro: |
| PLoS One. 2014 Dec 22;9(12):e115590. | | Enzymes from fungal and plant origin required for chemical diversification of insecticidal loline alkaloids in grass-Epichloë symbiota.[Pubmed: 25531527] |
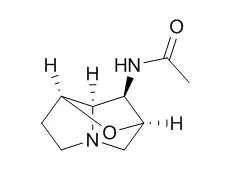
The lolines are a class of bioprotective alkaloids that are produced by Epichloë species, fungal endophytes of grasses. These alkaloids are saturated 1-aminopyrrolizidines with a C2 to C7 ether bridge, and are structurally differentiated by the various modifications of the 1-amino group: -NH2 (norloline), -NHCH3 (loline), -N(CH3)2 (N-methylloline), -N(CH3)Ac (N-acetylloline), -NHAc (N-Acetylnorloline), and -N(CH3)CHO (N-formylloline). Other than the LolP cytochrome P450, which is required for conversion of N-methylloline to N-formylloline, the enzymatic steps for loline diversification have not yet been established.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Through isotopic labeling, we determined that N-Acetylnorloline is the first fully cyclized loline alkaloid, implying that deacetylation, methylation, and acetylation steps are all involved in loline alkaloid diversification. Two genes of the loline alkaloid biosynthesis (LOL) gene cluster, lolN and lolM, were predicted to encode an N-acetamidase (deacetylase) and a methyltransferase, respectively. A knockout strain lacking both lolN and lolM stopped the biosynthesis at N-Acetylnorloline, and complementation with the two wild-type genes restored production of N-formylloline and N-acetylloline. These results indicated that lolN and lolM are required in the steps from N-Acetylnorloline to other lolines. The function of LolM as an N-methyltransferase was confirmed by its heterologous expression in yeast resulting in conversion of norloline to loline, and of loline to N-methylloline. One of the more abundant lolines, N-acetylloline, was observed in some but not all plants with symbiotic Epichloë siegelii, and when provided with exogenous loline, asymbiotic meadow fescue (Lolium pratense) plants produced N-acetylloline, suggesting that a plant acetyltransferase catalyzes N-acetylloline formation.
CONCLUSIONS:
We conclude that although most loline alkaloid biosynthesis reactions are catalyzed by fungal enzymes, both fungal and plant enzymes are responsible for the chemical diversification steps in symbio. | | Environ. Entomol., 2011, 40(3):639-47. | | Endophyte-mediated resistance to black cutworm as a function of plant cultivar and endophyte strain in tall fescue.[Pubmed: 22251642] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To improve Neotyphodium endophyte-mediated resistance to black cutworm Agrotis ipsilon (Hufnagel) (BCW), a series of experiments was conducted by using several different cultivars of tall fescue, Schedonorus arundinaceus (Schreb.) Dumort. in combination with several different haplotypes of the endophyte Neotyphodium coenophialum (Morgan-Jones & Gams) (plant cultivar × endophyte haplotype = plant line), each producing unique alkaloid profiles.
BCW settling response, survival at 5 and 10 d, and larval biomass varied significantly among plant lines. In general, greater variation BCW performance was observed within a single plant cultivar infected with different endophyte haplotypes than among different plant cultivars infected with the same endophyte haplotype, but comparisons among the former were far more numerous. Although five endophyte-mediated alkaloids representing three alkaloid classes were quantified in the plants, the pyrrolizidine alkaloid N-acetyl norloline was consistently the single best predictor of BCW performance. BCW settling response, 5-d survival, and 10-d survival decreased as levels of the alkaloid N-acetyl norloline increased. The same three response variables also decreased with increasing levels of peramine, but increased with increasing levels of ergovaline. Minor variation in endophyte infection levels occurring among infected plant lines had no significant influence on BCW performance.
CONCLUSIONS:
Results indicate a potentially important role for N-acetyl norloline and peramine in providing resistance to black cutworm whereas ergovaline appears to be much less important. Therefore, endophyte haplotypes expressing high levels of N-acetyl norloline and peramine may be of particular importance for developing 'friendly' endophyte-enhanced turf and pasture grasses that resist challenging lepidopteran pests, although remaining safe for wildlife and grazing mammals. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)