| In vitro: |
| Phytochemistry . 2020 Jul;175:112390. | | Gigantelline, gigantellinine and gigancrinine, cherylline- and crinine-type alkaloids isolated from Crinum jagus with anti-acetylcholinesterase activity[Pubmed: 32335411] | | Three undescribed Amarylidaceae alkaloids, named gigantelline, gigantellinine and gigancrinine, were isolated from Crinum jagus (syn. = Crinum giganteum) collected in Senegal, together with the already known sanguinine, cherylline, lycorine, crinine, flexinine and the isoquinolinone derivative hippadine. Gigantelline, gigantellinine and gigancrinine were characterized as 4-(6,7-dimethoxy-2-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-isoquinolin-4-yl)-phenol, its 7-O-demethyl-5ꞌ-hydroxy-4ꞌ-methoxy derivative and 5,6a,7,7a,8a,9-hexahydro-6,9a-ethano[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-j]oxireno[2,3-b]phenanthridin-9-ol, respectively, by using spectroscopic (1D and 2D 1H and 13C NMR and HRESIMS) and chemical methods. Their relative configuration was assigned by NOESY NMR spectra and NMR calculations, while the absolute configuration was assigned using electronic circular dichroism (ECD) experiments and calculations. Sanguinine, cherylline, crinine, flexinine, and the isoquinolinone hippadine, were isolated for the first time from C. jagus. Cherylline, gigantellinine, crinine, flexinine and sanguinine inhibited the activity of AChE in a dose-dependent manner, and inhibition by sanguinine was remarkably effective (IC50 = 1.83 ± 0.01 μM). Cherylline and hippadine showed weak cytotoxicity at 100 μM. | | Pharmacogenetics . 1999 Dec;9(6):661-668. | | The O-demethylation of the antidementia drug galanthamine is catalysed by cytochrome P450 2D6[Pubmed: 10634129] | | Galanthamine proved effective in symptomatic treatment of senile dementia of Alzheimer's type. The aim of this study was to elucidate the metabolism of galanthamine. Two novel metabolites of galanthamine have been isolated from the urine of eight young men after single doses of 10-15 mg. Some 19.8% of the doses were excreted as O-demethylgalanthamine glucuronide, 5% as N-demethylgalanthamine, 25.1% as galanthamine, and 0.8% as epigalanthamine. After coadministration of quinidine hydrogen sulfate, which inhibits cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) selectively, O-demethylgalanthamine glucuronide was highly diminished in urine. In vitro, human liver microsomes metabolized galanthamine to O-demethylgalanthamine with Vmax 5.2 nmol/mg protein/h and Km 187 microM. Ki of quinidine to inhibit O-demethylation was 28 nM. To inhibit cholinesterases, O-demethylgalanthamine was 10-fold more selective for acetylcholinesterase (AChE) versus butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE) than galanthamine. After glucuronidation, O-demethylgalanthamine failed to inhibit AChE and BuChE. N-Demethylgalanthamine inhibited cholinesterases less potently than galanthamine. | | Anticancer Agents Med Chem . 2019;19(5):707-717. | | Cytotoxic and Genotoxic Activities of Alkaloids from the Bulbs of Griffinia gardneriana and Habranthus itaobinus (Amaryllidaceae)[Pubmed: 30657047] | | Background: Amaryllidaceae plants are known to be a great source of alkaloids, which are considered an extensive group of compounds encompassing a wide range of biological activities. The remarkable cytotoxic activities observed in most of the Amaryllidaceae alkaloids derivatives have prompt the chemical and biological investigations in unexplored species from Brazil.
Objective: To evaluate the cytotoxic and genotoxic properties of alkaloids of Griffinia gardneriana and Habranthus itaobinus bulbs and study the role of caspase-3 as a molecular apoptosis mediator.
Methods: Methanolic crude extracts of Griffinia gardneriana and Habranthus itaobinus bulbs were submitted to acid-base extraction to obtain alkaloid-enriched fractions. The obtained fractions were fractionated using chromatographic techniques leading to isolation and identification of some alkaloids accomplished via HPLC and 1H-NMR, respectively. Molecular docking studies assessed the amount of free binding energy between the isolated alkaloids with the caspase-3 protein and also calculated the theoretical value of Ki. Studies have also been developed to evaluate in vitro cytotoxicity and genotoxicity in such alkaloids and apoptosis activation via the caspase pathway using both tumor and normal cell lines.
Results: Seven alkaloids were isolated and identified. Among these, 11-hydroxyvittatine and 2-α-7- dimethoxyhomolycorine were not cytotoxic, whereas tazettine, trisphaeridine, and sanguinine only showed activity against the fibroblast lineage. Lycorine and pretazettine were 10 to 30 folds more cytotoxic than the other alkaloids, including cancerous lines, and were genotoxic and capable of promoting apoptosis via the caspase-3 pathway. This result supports data obtained in docking studies wherein these two compounds exhibited the highest free energy values.
Conclusion: The cytotoxicity assay revealed that, among the seven alkaloids isolated, only lycorine and pretazettine were active against different cell lines, exhibiting concentration- and time-dependent cytotoxic actions alongside genotoxic action and the ability to induce apoptosis by caspase-3, a result consistent with those obtained in docking studies. | | Life Sci . 2002 Oct 11;71(21):2521-2529. | | Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity of some Amaryllidaceae alkaloids and Narcissus extracts[Pubmed: 12270757] | | Amaryllidaceous plants produce pharmacologically active alkaloids, galanthamine being the most interesting for its use in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease as a cholinesterase inhibitor. The aim of this work was to test 23 pure Amaryllidaceae alkaloids and 26 extracts from different species of the genus Narcissus for their acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity using galanthamine as a reference. Only seven alkaloids, belonging to the galanthamine and lycorine skeleton types, exhibited such an effect, sanguinine being the most active, even more than galanthamine. All the extracts with the highest acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity contained galanthamine except that of N. assoanus, a lycorine type alkaloid-bearing species. |
|


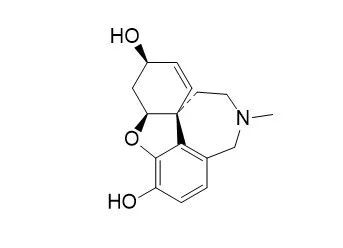



 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)