| In vitro: |
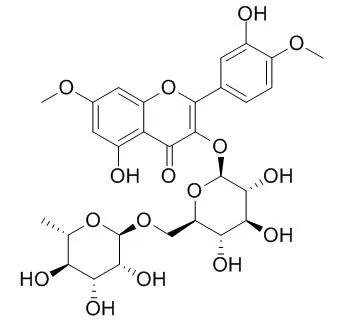
| Ann Pharm Fr. 1997;55(6):262-8. | | Isolation, identification and antimicrobial activity of ombuoside from Stevia triflora.[Pubmed: 9453171] | From aerial parts of Stevia triflora DC the flavonol glycoside Ombuoside (7,4'-di-O-methylquercetin-3-O-beta-rutinoside) has been isolated and identified on the basis of spectral data.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Ombuoside and the synthetic derivatives octa-acetylOmbuoside, ombuine and retusine were tested for antimicrobial activity against several strains of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and the yeast Candida albicans, using the agar diffusion method. The flavonol glycoside Ombuoside and the respective aglycone ombuine, both exhibited moderated activity against Corynebacterium diphtheria, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Candida albicans. To a lesser degree, octaacetylOmbuoside and retusine showed activity against the Gram-positive bacteria C. diphtheria and S. aureus, but proved to be inactive against Gram-negative bacteria and Candida albicans.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that the presence of free hydroxyl groups, either alcoholic or phenolic, is an important chemical feature for the expression of flavonol antimicrobial activity. It is worth noting that this is the first study reported on the antibacterial and antifungal activity of these substances. | | Fitoterapia. 2007 Jan;78(1):32-4. | | Antioxidant compounds from Ebenus pinnata.[Pubmed: 17067757] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Activity-guided fractionation of the methanol extract of Ebenus pinnata aerial parts led to the isolation of Ombuoside (1), kaempferol 3-O-rutinoside (2), rutin (3), catechin (4), and picein (5), along with beta-sitosterol and beta-sitosterol glucoside.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 1-4 showed significant antioxidant activity in the DPPH, and TEAC, reducing power assays. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)