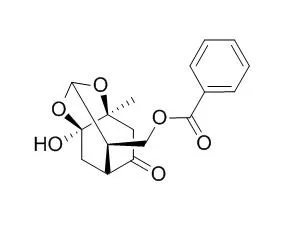
| Description: |
Paeoniflorigenone is a depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent, being similar to succinylcholine.Paeoniflorigenone is cytotoxic and induces apoptosis selectively in the cancer cell lines. Paeoniflorigenone shows anti-inflammatory effects, it may take part in improving blood circulation by inhibiting ether platelet aggregation and/or blood coagulation. |
| Targets: |
NO | Caspase |
| In vitro: |
| Pharmazie. 2010 Aug;65(8):624-8. | | Platelet anti-aggregatory and blood anti-coagulant effects of compounds isolated from Paeonia lactiflora and Paeonia suffruticosa.[Pubmed: 20824965] | The roots of two Paeoniaceae family members have long been used as traditional medicines in Korea, China, and Japan. Dry roots of Paeonia lactiflora and dry root bark of P. suffruticosa are used under the traditional names of Paeoniae Radix and Moutan Cortex, respectively.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Both Paeoniae Radix and Moutan Cortex have been used as remedies for cardiovascular diseases, for improving blood circulation, or for other uses. It was postulated that both plants may contain common active constituents that contribute to inhibiting blood coagulation and/or platelet aggregation. Eighteen compounds, which have been reported to be present in both plant medicines, were evaluated for their effects on platelet aggregation and blood coagulation.
CONCLUSIONS:
Paeonol (5), paeoniflorin (9), benzoylpaeoniflorin (11), and benzoyloxypaeoniflorin (12) were found to be the major common active constituents and they would collectively contribute to improving blood circulation through their inhibitory effects on both platelet aggregation and blood coagulation. In addition, methylgallate (4), (+)-catechin (7), Paeoniflorigenone (8), galloylpaeoniflorin (13), and daucosterol (16) may also take part in improving blood circulation by inhibiting ether platelet aggregation and/or blood coagulation. | | Bioscience Biotechnology & Biochemistry, 2017 :1-8. | | Apoptosis-inducing activity and antiproliferative effect of Paeoniflorigenone from moutan cortex[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Ninety samples from the extracts of plants from traditional Chinese medicines were screened for antitumor activity. Paeoniflorigenone (PFG) was isolated as an active ingredient from the root of moutan cortex, which showed the strongest activity. In addition, our data indicated that PFG was cytotoxic and induced apoptosis selectively in the cancer cell lines.
CONCLUSIONS:
These effects were cancelled by the addition of caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK, suggesting that it was mediated by caspase-3 activation. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Pharmaceutical Society of Korea, 2012,56(1):20-25. | | Anti-inflammatory effect of paeoniflorigenone isolated from Paeoniae Radix.[Reference: WebLink] | In Northeast Asia, Paeoniae Radix has been used in treatments of inflammation-causing diseases such as arthritis for many centuries. Paeoniflorin, one of the principle bioactive monoterpene glucosides from the paeony root, is reported to be mostly responsible for the effectiveness of the treatments. However, the anti-inflammatory effect of a monoterpene, Paeoniflorigenone (PFG) which partially has the moiety of paeoniflorin minus a glucose structure is unknown.
Thus, the aim of this work was to investigate anti-inflammatory activity of PFG.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
For the investigation, PFG activity on the NO (nitric oxide) prodn. from LPS-stimulated macrophages, and the anti-inflammatory effect was tested in the animal model of septic arthritis caused by Candida albicans, a major etiol. agent for septic arthritis. For induction of the arthritis, mice were administered with an emulsion of C. albicans cell wall (CACW) mixed with Complete Freund's Adjuvant (CFA) via footpad-injection (Day 0); PFG at a dose of 0.5 or 1 mg/mouse (25 or 50 mg/kg of body-wt.) was given to the animals on Day 3, 6, and 9; footpads were scored for arthritis. Moreover, the PFG effect on proliferation of T-lymphocyte that causes aggravation of arthritis was addnl. tested. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)