| In vitro: |
| Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Apr 29;408(1):18-24. | | Lucidenic acids-rich extract from antlered form of Ganoderma lucidum enhances TNFα induction in THP-1 monocytic cells possibly via its modulation of MAP kinases p38 and JNK.[Pubmed: 21453678 ] | The Ganoderma lucidum (G. lucidum) is one of the oriental fungi that has been reported to have immunomodulatory properties. Although effect of β-glucans from G. lucidum has been well documented, little is known about how other major bioactive components, the triterpenes, contribute to the immunomodulatory function of G. lucidum.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
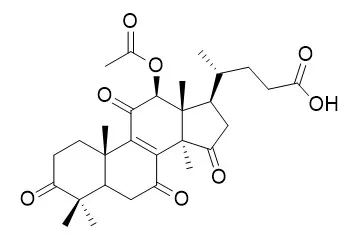
Here, we showed that triterpenes-rich extract of antlered form of G. lucidum (G. lucidum AF) induces TNFα production in monocytic THP-1 cells. Furthermore, the extract also synergized with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to induce TNFα production in THP-1 cells, suggesting an immunostimulatory role of triterpenes-rich extract of G. lucidum AF. Notably, the extract enhanced LPS-induced phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), while it suppressed LPS-induced phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) MAPK. p38 Inhibitor suppressed TNFα production, while JNK inhibitor enhanced TNFα production, implying that synergistic effect of the extract may work by modulating p38 and JNK MAPKs. Moreover, we found that the triterpenes-rich extract of G. lucidum AF contains high amounts of lucidenic acids. Lucidenic acid A, Lucidenic acid F and Lucidenic acid D2, which seem to dominantly exist in the extract, were purified from the triterpenes-rich extract. We also identified Lucidenic acid-A and -F as modulators of JNK and p38, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
Thus, our data demonstrate that lucidenic acids-rich extract from G. lucidum AF enhances LPS-induced immune responses in monocytic THP-1 cells possibly via the modulation of p38 and JNK MAPKs activation. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Planta Medica, 2015, 81(11). | | Biological activities of triterpenes isolated from the medicinal mushroom Ganoderma lucidum.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Methanol extract of Ganoderma lucidum subjected to fractionation on silica gel medium pressure column afforded over 40 fractions. Further fractionation was carried out using Centrifugal Partition Chromatography (FCPC Rousselet Robatel, France), in the hexane-EtOAc-MeOH-Water systems adjusted for the polarity of each fraction. Some isolates were further purified by preparative HPLC. Methyl esters of ganoderic and lucidenic acids were obtained by methylation of the acids. Twelve compounds, including ganoderic acid A (1), methyl ganoderate A (2), methyl lucidenate A (3), methyl lucidenate F (4), Lucidenic acid D2 (5), lucidenic acid A (6), lucidenic acid N (7), ganoderic acid DM (8), ganoderic acid F (9), ganoderic acid C (10), ganoderiol F (11) and ganodermonondiol (12) were evaluated for their biological activities. Antibacterial activity was determined against Gram -positive and -negative bacteria, anti-inflammatory effect against endotoxin (lipolysaccharide, LPS) induced inflammatory response in human macrophages, and anti-proliferative effects in human breast and colon cancer cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
We identified ganoderic acid DM as the most potent triterpene with anti-bacterial, anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative effects when compared to other Ganoderma isolates. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)