| Structure Identification: |
| Nat Prod Res. 2011 Aug;25(14):1361-5. | | A new hydrochalcone from Miliusa sinensis.[Pubmed: 21859261] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
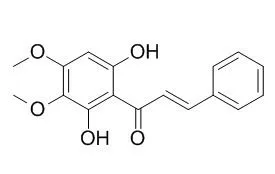
A new dihydrochalcone 4',6'-dihydroxy-2',3',4-trimethoxydihydrochalcone (1) along with nine known compounds, Pashanone (2), dihydroPashanone (3), pinostrobin (4), 5-hydroxy-7,4'-dimethoxyflavanone (5), 5-hydroxy-6,7-dimethoxyflavanone (6), 5-hydroxy-7,8-dimethoxyflavanone (7), 24-methylencycloartane-3β,21-diol (8), liriodenine (9) and 3,5-dihydroxy-7,3',4'-trimethoxyflavone (10), were isolated from the extracts, exhibiting cytotoxic activity (n-hexane and ethyl acetate extracts) of Miliusa sinensis.
CONCLUSIONS:
The structure of (1) was elucidated by the analysis of spectral data (IR, HR-MS, EI-MS, 1D and 2D NMR). | | Phytochemistry. 2006 Oct;67(19):2152-8. | | An unusual homoisoflavanone and a structurally-related dihydrochalcone from Polygonum ferrugineum (Polygonaceae).[Pubmed: 16884749] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The homoisoflavanone 5,7-dihydroxy-6-methoxy-3-(9-hydroxy-phenylmethyl)-chroman-4-one (1) and its structurally related 2',4',6'-trihydroxy-3'-methoxy-alpha-hydroxymethyl-beta-hydroxy-dihydrochalcone (2) along with the known Pashanone (3), flavokawin B (4) and cardamonin or alpinetin chalcone (5) pinostrobin (6) and 5,8-dimethoxy-7-hydroxychroman-4-one (7) were isolated from dry leaves of Polygonum ferrugineum (Polygonaceae).
CONCLUSIONS:
To our knowledge, this is the first report of the isolation of a homoisoflavanone from the Polygonum genus and the Polygonaceae family, and could be an important chemotaxonomic finding. In addition, the pattern of substitution of this homoisoflavanone is different from others previously reported. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)