| Kinase Assay: |
| Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(6):938-45. | | Citreorosein inhibits production of proinflammatory cytokines by blocking mitogen activated protein kinases, nuclear factor-κB and activator protein-1 activation in mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells.[Pubmed: 22687535] | Citreorosein (CIT), an anthraquinone component of Polygoni cuspidati (P. cuspidati) radix, suppressed gene expression of proinflammatory cytokines including tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-1β in mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells (BMMCs) stimulated with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) plus the calcium ionophore A23187.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying Citreorosein inhibition of the pro-inflammatory cytokine production, its effects on the activation of both nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) were assessed. Citreorosein attenuated phosphorylation of the MAPKs including extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), p38 MAP kinase and c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK). Furthermore, Citreorosein strongly inhibited DNA binding activity of NF-κB through the inhibition of phosphorylation and degradation of inhibitor of kappaB (IκB) as well as activator protein-1 (AP)-1 through the reduction of phosphorylation of c-Jun.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results demonstrate that Citreorosein inhibits proinflammatory cytokines production through the inhibition of both MAPKs and AKT-mediated IκB kinase (IKK) phosphorylation and subsequent inhibition of transcription factor NF-κB activation, thereby attenuating the production of proinflammatory cytokines. | | Food Chem Toxicol. 2012 Mar;50(3-4):913-9. | | Citreorosein, a naturally occurring anthraquinone derivative isolated from Polygoni cuspidati radix, attenuates cyclooxygenase-2-dependent prostaglandin D2 generation by blocking Akt and JNK pathways in mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells.[Pubmed: 22154852] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we examined the effects of Citreorosein (CIT), an anthraquinone component of Polygoni cuspidati radix (P. cuspidati, Polygonaceae), on cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 dependent prostaglandin (PG)D2 generation in mast cells, central effector cells of allergy and other inflammatory diseases. Citreorosein strongly inhibited COX-2-dependent PGD2 generation in a concentration-dependent manner in mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells (BMMCs) stimulated with stem cell factor (SCF)/IL-10/LPS. In an effort to identify the mechanisms underlying the inhibition of COX-2-dependent PGD2 generation by Citreorosein, we examined the effects of this compound on MAP kinases, Akt and NF-κB signaling pathways, which are essential for COX-2 induction. Citreorosein inhibited nuclear translocation of the nuclear factor (NF)-κB p65 subunit and its cognate DNA-binding activity, which correlated with its inhibitory effects on the phosphorylation of Akt and IKK and subsequent phosphorylation and degradation of IκB. Furthermore, Citreorosein significantly attenuated the DNA binding of activator protein (AP)-1 that regulates COX-2 expression through the reduction of the phosphorylation of c-Jun. Moreover, inhibition of PGD2 generation by Citreorosein was accompanied by a decrease in phosphorylation of cytosolic phospholipase A2α.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, the present study suggests that Citreorosein represents a potential therapeutic approach for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. |
|
| Structure Identification: |
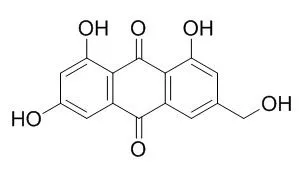
| Arch Pharm Res. 2012 Mar;35(3):447-54. | | A facile synthesis of emodin derivatives, emodin carbaldehyde, citreorosein, and their 10-deoxygenated derivatives and their inhibitory activities on μ-calpain.[Pubmed: 22477191] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A new procedure for the preparation of emodin carbaldehyde and Citreorosein was described, in which, ω,ω'-dibromomethylemodin triacetate was prepared as a key intermediate by NBSmediated bromination of 1,3,8-triacetylemodin. Reduction of emodin and Citreorosein with SnCl(2) in a 1:1 mixture of HOAc and HCl afforded the corresponding anthrones in 90% and 92% yield, respectively, while the corresponding 10-desoxyemodin carbaldehyde was prepared by MnO(2) oxidation of 10-desoxyCitreorosein.
CONCLUSIONS:
10-DesoxyCitreorosein and emodin carbaldehyde showed feasible μ-calpain inhibitory activities with IC(50) values of 20.15 and 25.77 M, respectively. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)