| Animal Research: |
| Chinese Traditional & Herbal Drugs, 2013, 44(11):1455-9. | | Protection of peimisine on hepatic fibrosis of rats induced by CCl4.[Reference: WebLink] | To investigate the protective effect of Peimisine on carbon tetrachloride(CCl4)-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The rats were divided into control,model,low-,mid-,and high-dose(2.5,5,and 10 mg/kg) Peimisine groups.Hepatic fibrosis models were induced by ip injection of CCl4 in rats once every 3 d for 8 weeks.The rats in the treatment groups were administered four weeks after the model establishment,once daily until the end of the week 4 after the model establishment.The levels of serum alanine aminotransferase(ALT),aspartate aminotransferase(AST),alkaline phosphatase(ALP),glutamyl transpeptidasecc(GGT),hyaluronie acid(HA),laminin(LN),type III procollagenc(PC-III),and collegen type IV(IV-C) were assayed,and hepatic tissue contents of hydroxyprolinc(Hyp),superoxide dismutase(SOD),and malondialdehyde(MDA) were determined.The effect of Peimisine on hepatic fibrosis in rats was observed. Compared with the model control group,the hepatic fibrosis of rats in Peimisine groups was improved obviously,the levels of ALT,AST,ALP,and GGT in serum were lowered obviously(P 0.05,0.01),also the serum levels of HA,LN,PC-III,IV-C,and the contents of Hyp and MDA in liver tissue were decreased(P 0.01),while the level of SOD was increased(P 0.01).
CONCLUSIONS:
Peimisine has the protective effect on the experimental hepatic fibrosis formation.The possible mechanisms are associated with inhibiting fibrogenesis and fibrosis accumulation,and decreasing lipid peroxidation. |
|
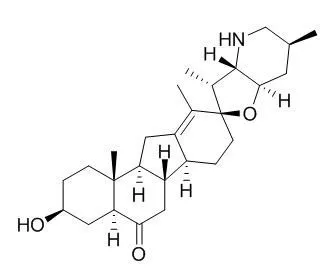
| Structure Identification: |
| Planta Med. 2003 Jun;69(6):564-5. | | Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory alkaloids from Fritillaria ussuriensis.[Pubmed: 12865981 ] | Bioassay-guided fractionation of the BuOH-soluble extract of Fritillaria ussuriensis afforded verticinone ( 1), verticine ( 2), and Peimisine ( 3). Purification of these compounds was achieved with the use of various chromatographic methods.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The structures of the compounds were identified on the basis of MS and NMR data analysis. Compounds 1 - 3 inhibited angiotensin I converting enzyme activity in a dose-dependent manner, displaying 50 % inhibitory concentration values of 165.0 microM, 312.8 microM, 526.5 microM, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
The presence of these active substances may be responsible, at least in part, for the antihypertensive action of the bulbs of Fritillaria ussuriensis. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)